Chapter 17
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
By Boundless
The heart is an organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels using rhythmic contractions of cardiac muscle.

The pericardium is a thick, membranous, fluid-filled sac which encloses, protects, and nourishes the heart.
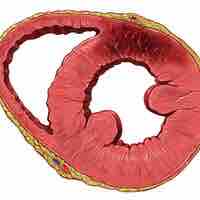
The heart wall is comprised of three layers: the outer epicardium, the middle myocardium, and the inner endocardium.
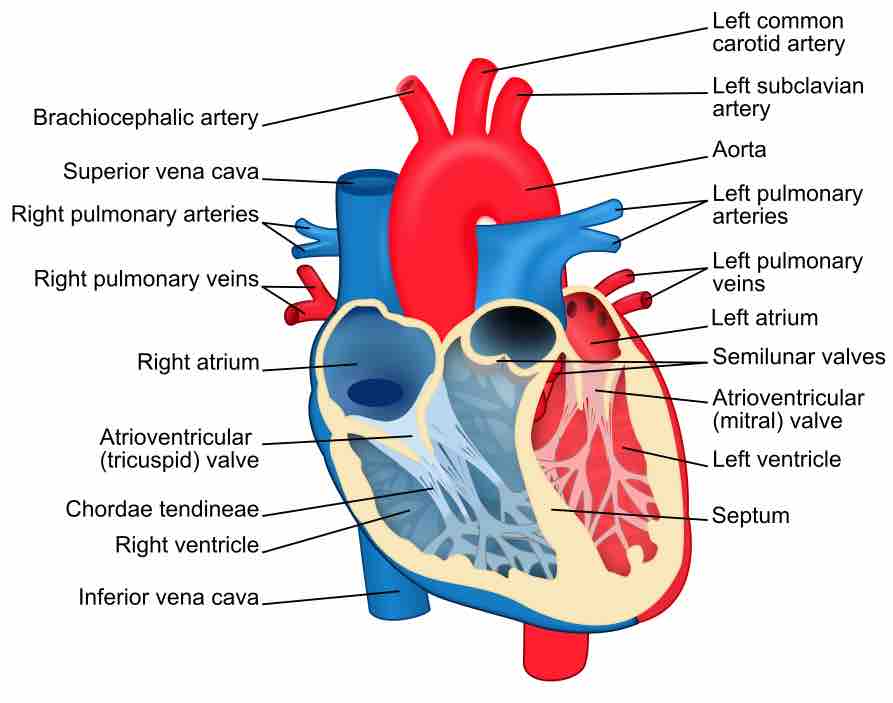
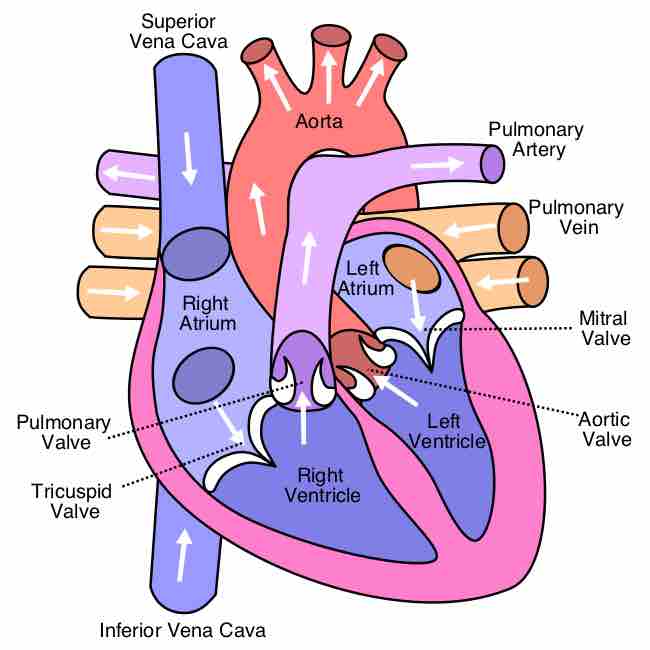
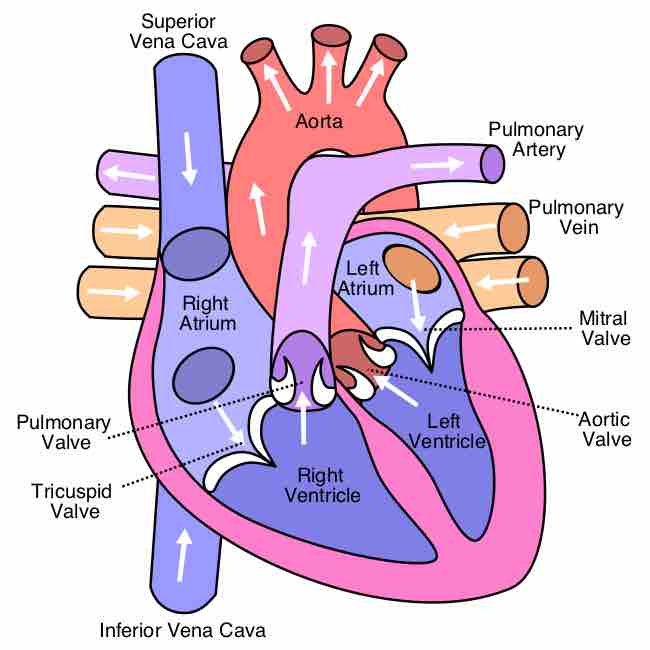
The heart has four chambers. The two atria receive blood into the heart and the two ventricles pump blood into circulation.
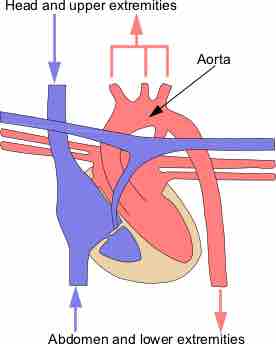
Great vessels are the major vessels which directly carry blood into or out of the heart.

The myocardium (cardiac muscle) is the thickest section of the heart wall and contains cardiomyocytes, the contractile cells of the heart.
The cardiac skeleton, also known the heart's fibrous skeleton, consists of dense connective tissue in the heart that separates the atria from the ventricles.
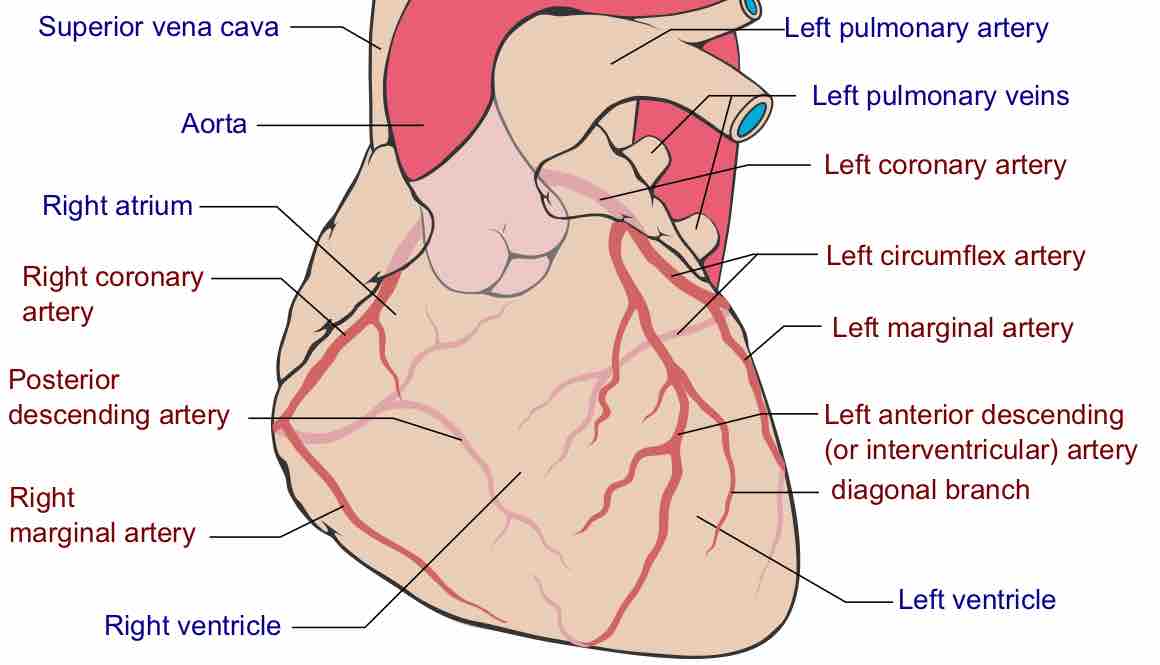
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels of the heart.
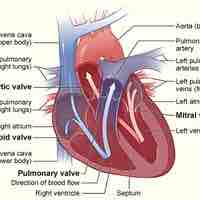
The atrioventricular valves separate the atria from the ventricles and prevent backflow from the ventricles into the atria during systole.
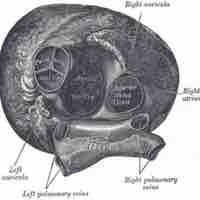
The semilunar valves allow blood to be pumped into the major arteries, but prevent backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles.

The cardiovascular system has two distinct circulatory paths, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
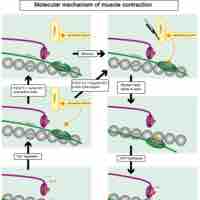
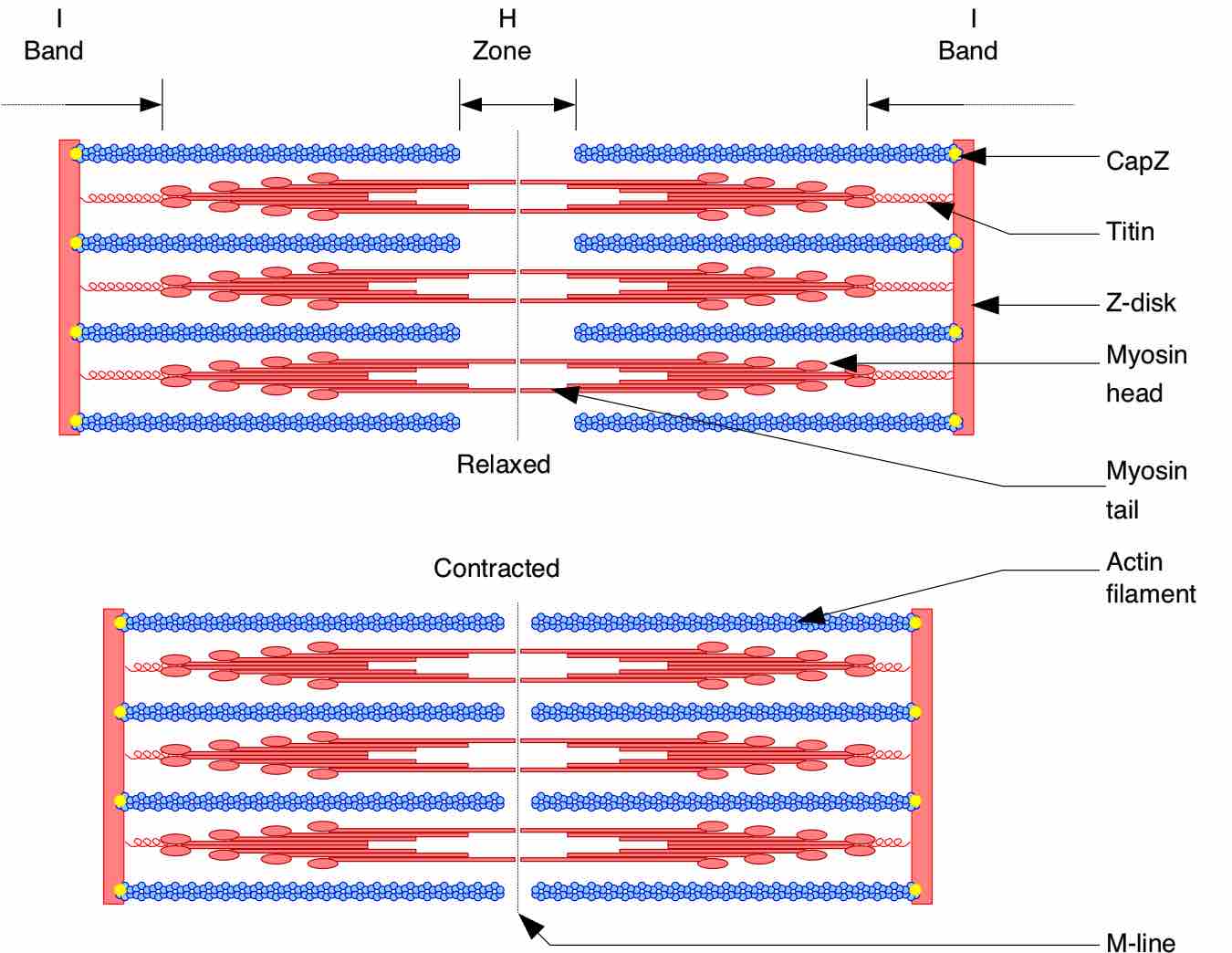
Cardiac muscle appears striated due to the presence of sarcomeres, the highly-organized basic functional unit of muscle tissue.
Cardiac muscle fibers undergo coordinated contraction via calcium-induced calcium release conducted through the intercalated discs.
Cardiac cells contain numerous mitochondria, which enable continuous aerobic respiration and production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for cardiac function.
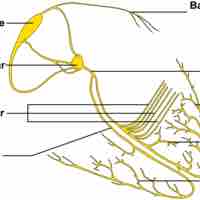
Cardiac contraction is initiated in the excitable cells of the sinoatrial (SA) node by both spontaneous depolarization and sympathetic activity.
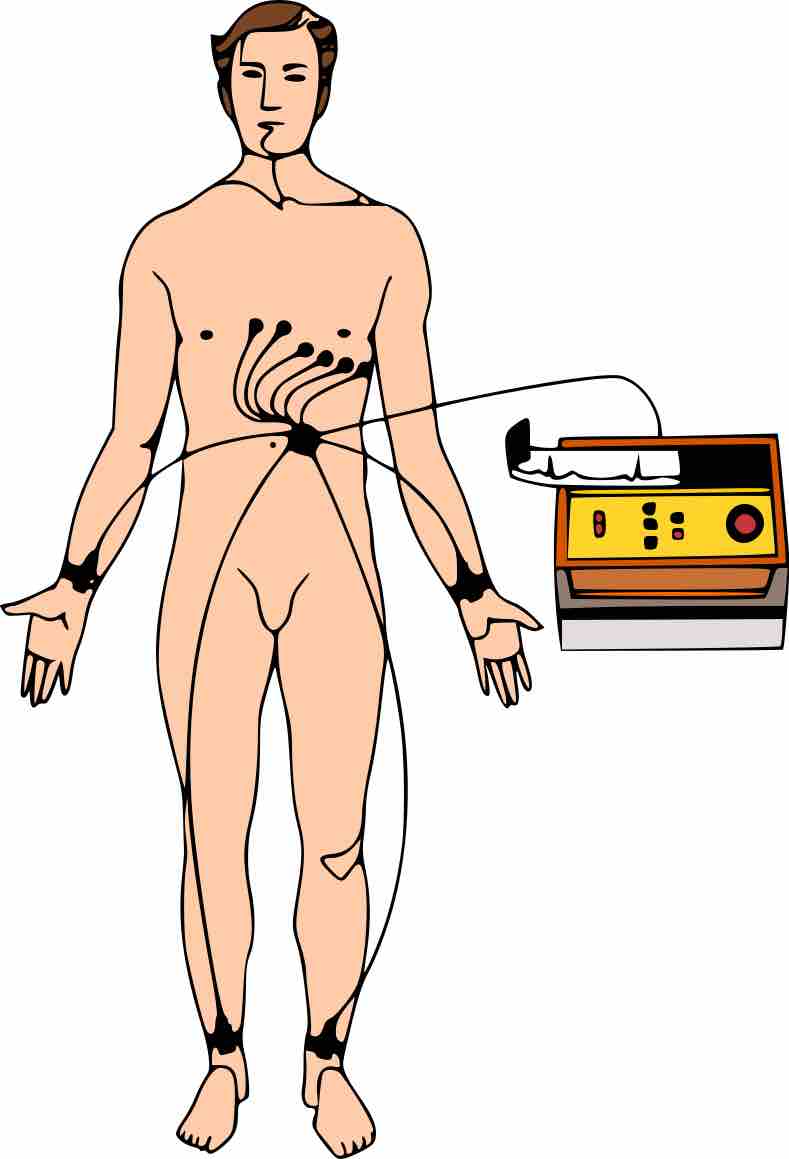
An electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a recording of the heart's electrical activity as a graph over a period of time.
The two major heart sounds are "lub" (from the closure of AV valves) and "dub: (from the closure of aortic and pulmonary valves).
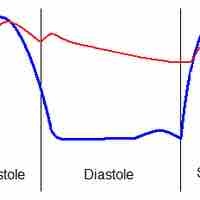
The cardiac cycle describes the heart's phases of contraction and relaxation that drive blood flow throughout the body.
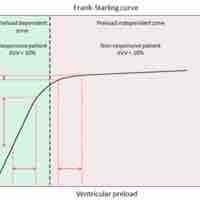
Cardiac output (Q or CO) is the volume of blood pumped by the heart, in particular by the left or right ventricle, in one minute.