Chapter 10
Epidemiology
By Boundless
Epidemiology is the study of the patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease conditions in defined populations.

Epidemiological studies include disease etiology, disease surveillance and screening, biomonitoring, and clinical trials.

Epidemiology is the study of the patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease conditions in set populations.

Koch's postulates are four criteria designed in the 1880's to establish a causal relationship between a causative microbe and a disease.

Even in Koch's time, it was recognized that infectious agents could be responsible for disease without fulfilling all of the postulates.

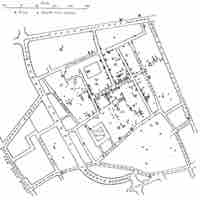
An occurrence of disease greater than would be expected at a particular time and place is called an outbreak.
The severity and duration of diseases vary greatly and are important for epidemiological studies.
Host-pathogen interactions are the interactions taking place between a pathogen (e.g. virus, bacteria) and their host (e.g. humans, plants).

Modern nucleic acid-based microbial detection methods make it possible to identify microbes that are associated with a disease.

The spread and severity of infectious disease is influenced by many predisposing factors.
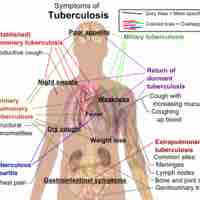
After an pathogen invades a host, it undergoes a series of phases that eventually lead to multiplication of the pathogen.
Once discovered, natural reservoirs elucidate the complete life cycle of infectious diseases, providing effective prevention and control.

Defining the means of transmission of a pathogen is important in understanding its biology and in addressing the disease it causes.
Pathogens have evolved to adapt to their environment and their host in order to survive.

Working with microorganisms, especially pathogens, requires special equipment and safety practices.

The index case is identified in epidemiology studies by tracking down the infected patients to try to determine how the disease originated.
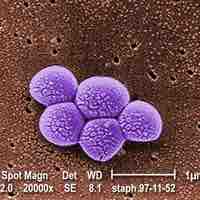
Nosocomial infections can cause severe pneumonia and infections of the urinary tract, bloodstream, and other parts of the body.

Numerous risk factors in the hospital setting can predispose a patient to infection.
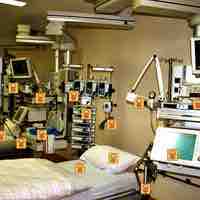
The most important and frequent mode of transmission of nosocomial infections is by direct contact.

Hospitals have sanitation protocols regarding uniforms, equipment sterilization, washing, and other preventive measures.
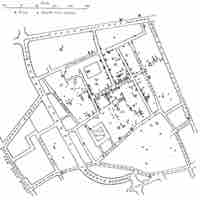
Descriptive epidemiology focuses on describing disease distribution by characteristics relating to time, place, and people.

Epidemiology draws statistical inferences, mostly about causes of disease in populations based on available samples of it.
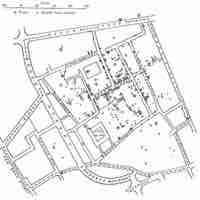
Experimental epidemiology uses an experimental model to confirm a causal relationship suggested by observational studies.

Promotion of hand washing, breastfeeding, delivery of vaccinations, and distribution of condoms are examples of public health measures.

Global health is the health of populations in a global context and transcends the perspectives and concerns of individual nations.
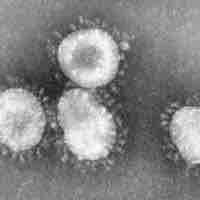
An emerging infectious disease is a disease with a rate of incidence that has increased in the past 20 years, and could increase in the near future.

Biological warfare (BW) is the use of biological toxins or infectious agents with the intent to kill or incapacitate.
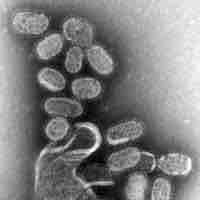
Technology aids in the identification of new infectious agents, but it also contributes to the emergence of new diseases.
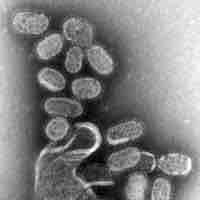
An epidemic occurs when new cases of a disease, in a given human population, and during a given period, substantially exceed expectations.
- Overview of Viruses
- Structure of Viruses
- Classifying Viruses
- Culturing Viruses
- Viral Replication