Changes in Temperature
Changes in temperature can affect the equilibrium state of a reversible chemical reaction. The effect of changes to the equilibrium state can be predicted using Le Chatelier's Principle. Le Chatelier's Principle states that when changes are made to a reversible chemical reaction in equilibrium, the system will compensate for that change with a predictable, opposing shift. This law can be applied to changes in pressure, volume, concentration, and temperature.
Reactions can be classified by their enthalpies of reaction. Reactions with positive enthalpies—those that absorb heat from their surroundings—are known as endothermic. In contrast, reactions with negative enthalpies—those that release heat into their surroundings—are known as exothermic. A diagram of the reaction coordinate for an exothermic reaction is shown in .
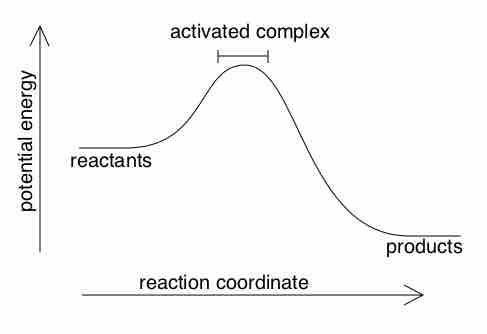
Exothermic Reaction
Reaction coordinate for an exothermic reaction
Le Chatelier's Principle predicts that the addition of products or the removal of reactants from a system will reverse the direction of a reaction, while the addition of reactants or the removal of products from a system will push the reaction towards the formation of products.
Applied to temperature, Le Chatelier's Principle predicts that the addition of heat to a system will cause an opposing reaction in the system to remove heat. Exothermic reactions will be shifted toward the reactants. Endothermic reactions, on the other hand, will be shifted towards product formation as heat is removed from the reaction's surrounding environment.