Chapter 6
Early Civilizations in the Indian Subcontinent
By Boundless
The Indus River Valley Civilization, located in modern Pakistan, was one of the world’s three earliest widespread societies.
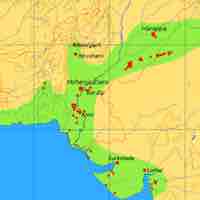
The Indus River Valley Civilization (IVC) contained urban centers with well-conceived and organized infrastructure, architecture, and systems of governance.
The Indus River Valley Civilization, also known as Harappan, included its own advanced technology, economy, and culture.
The Indus Valley Civilization declined around 1800 BCE due to climate change and migration.

Different theories explain the Vedic Period, c. 1200 BCE, when Indo-Aryan people on the Indian subcontinent migrated to the Ganges Plain.
A caste system developed among Indo-Aryans of the Vedic Period, splitting society into four major groups.
Vedic Sanskrit evolved to Classical Sanskrit, which has influenced modern Indian languages and is used in religious rites.
The Vedas are the oldest texts of the Hindu religion and contain hymns, myths and rituals that still resonate in India today.
Hinduism evolved as a synthesis of cultures and traditions, including the Indo-Aryan Vedic religion.
Sramana broke with Vedic Hinduism over the authority of the Brahmins and the need to follow ascetic lives.
After attaining Enlightenment, Siddhartha Gautama became known as the Buddha, and taught a Middle Way that became a major world religion, known as Buddhism.
Jainism is a pre-Buddhist religion with roots in the Sramana tradition. It focuses on karma.
Under Cyrus the Great and Darius the Great, the Achaemenid Empire became the first global empire.
Emperors Cyrus II and Darius I created a centralized government and extensive trade network in the Achaemenid Empire.
Zoroastrianism, an ancient Persian religion, had a major influence on the culture and religion of all other monotheistic religions in the region.
Chandragupta Maurya founded the Maurya Empire in 322 BCE when he conquered the kingdom of Magadha and the northwestern Macedonian satrapies.
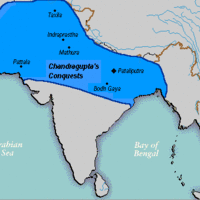
After winning the Seleucid-Mauryan war, the Maurya Empire expanded into the southern Indian subcontinent under the rule of Ashoka the Great.

The Mauryan Empire encouraged economic prosperity through political stability and a unified central government.
Mauryan emperor Ashoka embraced Buddhism after witnessing the mass deaths of the Kalinga War, which he himself had waged out of a desire for conquest.
The Sunga Dynasty usurped the Maurya Dynasty, and parts of the empire were incorporated into the Indo-Greek Kingdom.
From 320-550 CE, the Gupta Empire assimilated neighboring kingdoms, through conquest or political alliances.
The prosperity of the Gupta Empire produced a golden age of cultural and scientific advancements.
After many years of dominance, the Gupta Empire collapsed in 550 CE, due to invasions and weak leadership of successive rulers.