Chapter 2
Ancient Mesopotamian Civilizations
By Boundless
The Sumerian people lived in Mesopotamia from the 27th-20th century BCE. They were inventive and industrious, creating large city-states, trading goods, mass-producing pottery, and perfecting many forms of technology.
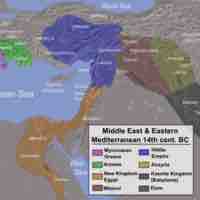
The Assyrians were a major Semitic empire of the Ancient Near East, who existed as an independent state for approximately nineteen centuries between c. 2500-605 BCE, enjoying widespread military success in its heyday.
The first civilizations formed in river valleys, and were characterized by a caste system and a strong government that controlled water access and resources.

The Akkadian Empire flourished in the 24th and 22nd centuries BCE, ruled by Sargon and Naram-Sin. It eventually collapsed in 2154 BCE, due to the invasion of barbarian peoples and large-scale climatic changes.
The city-state of Ur in Mesopotamia was important and wealthy, and featured highly centralized bureaucracy. It is famous for the Ziggurat of Ur, a temple whose ruins were discovered in modern day.

Following the collapse of the Akkadians, the Babylonian Empire flourished under Hammurabi, who conquered many surrounding peoples and empires, in addition to developing an extensive code of law and establishing Babylon as a "holy city" of southern Mesopotamia.
The Code of Hammurabi was a collection of 282 laws, written in c. 1754 BCE in Babylon. Many of the laws focused on contracts and family relationships, and they featured a presumption of innocence and the presentation of evidence.
Hallmarks of Babylonian culture include mudbrick architecture, extensive astronomical records and logs, diagnostic medical handbooks, and translations of Sumerian literature.
The Kassite Dynasty ruled Babylonia following the fall of Hammurabi and was succeeded by the Second Dynasty of Isin, during which time the Babylonians experienced military success and cultural upheavals under Nebuchadnezzar.