Chapter 19
The Progressive Era: 1890–1917
By Boundless

The Progressive Era was a period of social activism and political reform in the United States that flourished from the 1890s to the 1920s.
Progressive-Era reformers sought to use the federal government to make sweeping changes in politics, education, economics, and society.

The Social Gospel movement applied Christian ethics to social problems.
The end of the Gilded Age witnessed rising levels of social criticism from a new kind of investigative journalist called a "muckraker."
Early efforts in urban reform were driven by poor conditions exposed by tragedies such as the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire.
The Settlement House movement was a reform that intended for the rich and the poor to live together in interdependent communities.

Maternalist reforms provided assistance for mothers and children, expanding the American welfare state.
Progressives sought to enable the citizenry to rule more directly.

Progressive reformers tried to apply scientific principles and rational problem-solving to social problems.

Progressive reformers regarded regulation as a cure for all sorts of socioeconomic and political problems.
Prohibition was a major reform movement from the 1840s into the 1920s. Its goal was to prohibit the manufacture or sale of alcohol.
The term "first-wave feminism" describes the women's movements during the Gilded Age, which primarily focused on women's suffrage.

The movement for women's suffrage gained new vitality during the Progressive Era.

After attaining suffrage, women extended their activism to focus on contraception, sexual autonomy, and economic rights.

Theodore Roosevelt's presidency was a driving force for the Progressive movement in the United States in the early twentieth century.

A major part of Roosevelt's legacy is his conception of the executive branch as a source of regulatory powers for the "good" of the nation.

Roosevelt's Square Deal focused on conservation of natural resources, control of corporations, and consumer protection.

Roosevelt's big-stick diplomacy refers to negotiating peacefully with other nations while simultaneously displaying military might.
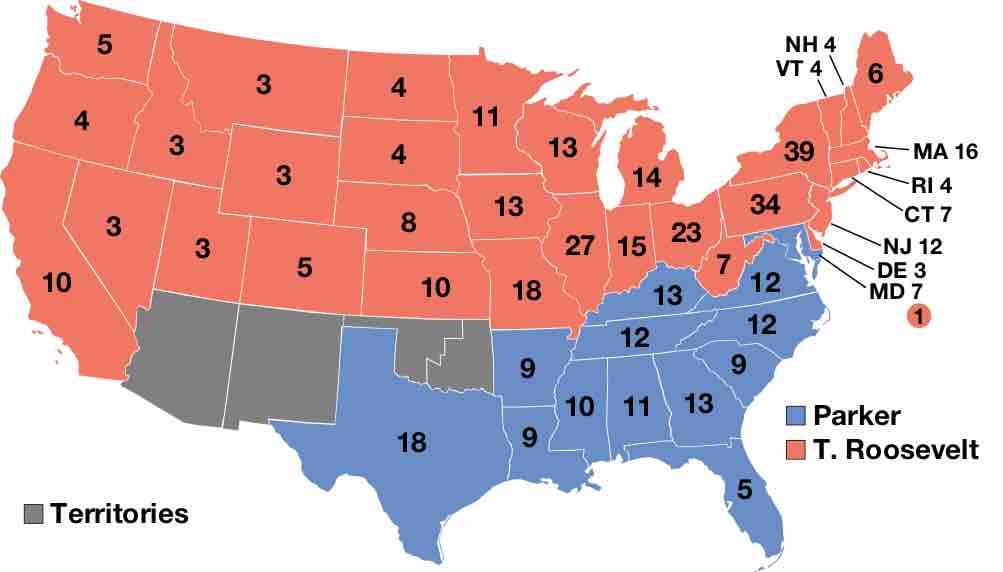
In 1904, Theodore Roosevelt won a landslide victory for his re-election, enabling him to pursue a number of bold Progressive reforms.
Theodore Roosevelt embraced legislation aimed at conserving the natural environment.

In 1908, Theodore Roosevelt persuaded the Republican Party to nominate William Howard Taft to run against Democratic candidate William Jennings Bryan.

In 1908, Republicans promised to lower unpopular tariffs on U.S. imports, but the Payne-Aldrich Tariff Act further divided Republicans.

The Pinchot-Ballinger Controversy was a dispute between U.S. Forest Service Chief Gifford Pinchot and Secretary of the Interior Richard Ballinger.

Defeating Theodore Roosevelt's third-party "Bull Moose" candidacy in 1912, Wilson went on to enact sweeping Progressive reforms of his own.
During his first term as President, Wilson focused on three types of reform: Tariff Reform, Banking Reform, and Business Reform.

Although the Progressive Era was a period of social progress, it also had multiple, contradictory goals that impeded reform efforts.

African-Americans, immigrants from Asia, and Native Americans were largely excluded from the focus of Progressive reform.