Chapter 10
Democracy in America: 1815–1840
By Boundless

Republican Motherhood, while maintaining women's role in the private sphere, gave women more rights to education.
During the early nineteenth century, women were mainly relegated to the private sphere through the "cult of domesticity."

While women gained some legal rights in the nineteenth century, African-American women, in particular, remained largely disenfranchised.

In the early nineteenth century, large discrepancies existed between the educational opportunities for men and women.

The U.S. presidential election of 1816 resulted in an easy win for James Monroe and ushered in the "Era of Good Feelings."

The "Era of Good Feelings" marked a period that reflected a sense of national purpose and a desire for unity at the end of the War of 1812.
The Panic of 1819 was the first major financial crisis in the U.S. and occurred during the political calm of the Era of Good Feelings.

The Missouri Compromise of 1820 concerned the regulation of slavery in the western territories.

The Monroe Doctrine opposed efforts by European nations to colonize land or interfere with states in North or South America.

John Quincy Adams was elected president by the House of Representatives in 1824, despite not winning the popular vote.

John Quincy Adams, sixth president of the United States, served from March 4, 1825, to March 4, 1829.
The Second Party System, consisting largely of the Democrats and Whigs, contributed to rising levels of voter investment and partisanship.
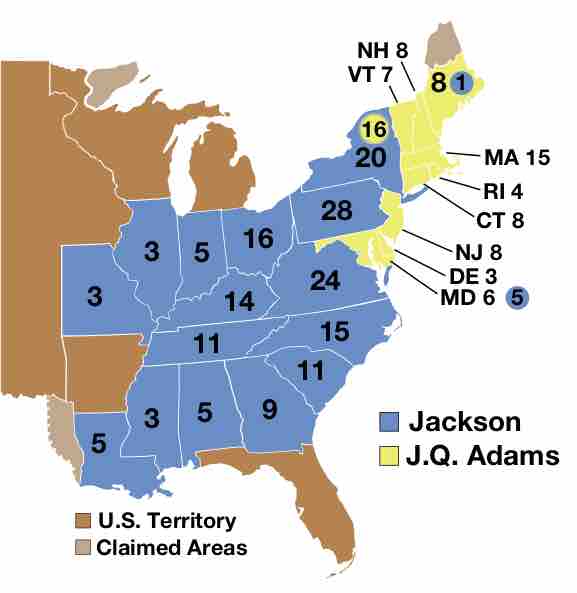
The election of 1828 between John Quincy Adams and Andrew Jackson saw a large number of character attacks and increased partisanship.

Andrew Jackson's presidency was a highly controversial period characterized by Jacksonian democracy and the rise of the common man.
The modern Democratic Party arose in the 1830s out of factions from the largely disbanded Democratic-Republican Party.

While the spoils system of awarding government jobs to political supporters had existed for a long time, it was greatly popularized under Andrew Jackson.
The Tariff of 1828 highlighted economic conflicts of interest between the Northern and Southern states that eventually led to the Nullification Crisis of 1832.

The Indian Removal Act of 1830 set the stage for the forced relocation of American Indians from the east to the west.

The movement toward white male suffrage was expanded during Jackson's presidency before the American Civil War.

The Dorr Rebellion in Rhode Island was an uprising of men who wanted to see greater, faster expansion of white male suffrage.

The American System advocated industrial, physical, and financial infrastructure, as well as support for public education.

The Second Bank of the United States functioned from 1816 until 1836, when it came under attack by Jacksonian Democrats.

During the early years of the United States, protective tariffs were put in place to aid the new nation's economy; however, the taxes caused tension in the South.
The Marshall Court established the legal authority of the Supreme Court over the states and other branches of the federal government.
During John Marshall's 34-year tenure as chief justice, a number of important Supreme Court decisions defined the federal government's role and powers.

While most Northerners were indifferent to slavery or opposed it for economic reasons, a growing number of abolitionists viewed slavery as immoral.

The financial crisis of 1837 was based on speculative fever and contributed to a five-year economic depression.