Introduction: The Middle Colonies
The Middle Colonies tended to mix aspects of the New England and Southern Colonies. Families generally held and worked plots of between 40 and 160 acres. In New York's Hudson Valley, however, the Dutch established the patroon system, which resembled a feudal aristocracy governing vast land grants. The title of patroon was given to some of the Dutch colony's invested members, who operated very large landed estates and rented land to tenant farmers. Indentured servitude was especially common in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York in the 18th century, though few such servants worked in agriculture.
Varied Origins of Middle Colonials
American Indian tribes had long occupied the area that was conquered as the British Middle Colonies. These tribes included the Mohawk, Mahican, Algonquian Lenape, Wecquaesgeek, Hackensack, Raritan, Canarsee, and Tappan. Munsee inhabited the Highlands, Hudson Valley, and northern New Jersey, while Minquas, also known as the Susquehannocks, lived west of the Zuyd River along and beyond the Susquehanna River.
Once colonization had begun, the Middle Colonies were more ethnically diverse than the other British colonial regions in North America and tended to be more socially tolerant. For example, in New York, any foreigner professing Christianity was awarded citizenship, which made for a diverse (albeit largely Christian) populace. As a consequence, early settlements of Germans from many different sects concentrated in the Middle Colonies. German immigration greatly increased around 1717, and many immigrants began coming from the Rhineland in western Germany. They were erroneously labeled the Pennsylvania Dutch and comprised one-third of the population by the time of the American Revolution. The industry and farming skills they brought with them helped solidify the Middle Colonies' prosperity. They were noted for tight-knit religious communities, which were often Lutheran.
The Scots-Irish also began immigrating to the Middle Colonies in waves after 1717. They primarily pushed farther into the western frontier of the colonies, where they repeatedly confronted American Indians. Other groups included the Welsh, Dutch, Swedes, Swiss, Scots Highlanders, and Huguenots. By 1780, about 17% of the population in New York were descendants of Dutch settlers; the rest were mostly English with a wide mixture of other Europeans and about 6% Africans. New Jersey and Delaware had a majority British population as well, with 7–11% German-descended colonists, about a 6% African population, and a small contingent of Swedish descendants.
Slavery in the Middle Colonies
The Dutch West India Company introduced slavery to New Netherland in 1625. When the colony fell to the British, the Company freed all of its slaves, establishing early on a nucleus of free Africans in the Northeast. In an early attempt to encourage European settlement, the New Jersey legislature enacted a prohibitive tariff against imported slaves and in favor of European indentured servitude. Despite Quaker opposition to slavery, by 1730, colonists had brought about 4,000 slaves into Pennsylvania. The Pennsylvania Gradual Abolition Act of 1780 was the first attempt to abolish slavery in the colonies and what would become the United States.
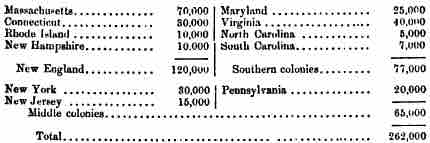
Population in 1700
Estimated population in the Colonies as of the year 1700. The Middle Colonies held a population of about 65,000, compared to New England's 120,000 and the Southern Colonies' 77,000.