Chapter 14
Religion
By Boundless

Religion is a collection of cultural systems, belief systems, and worldviews that relate humanity to spirituality and to moral values.

A conventional social scientific view understands religion as a group's collective beliefs and rituals relating to the supernatural.

Supernaturalism refers to any belief system with supernatural forces, such as magic, and, in general, is prevalent in all societies.

Animism is the belief that non-human entities are spiritual beings, either intrinsically or because spirits inhabit them.

Theism refers to any belief system that incorporates a deity.
Emile Durkheim posited the sacred–profane dichotomy as central to all religion, but critics suggest this theory is too eurocentric.

Karl Marx argues that religion works to calm uncertainty over our role in the universe and in society, and to maintain the status quo.

Marx viewed religion as a tool of social control used by the bourgeoisie to keep the proletariat content with an unequal status quo.

Religious symbolism is the use of acts, artwork, and events to create a mythos expressing the teachings of the religion.

A ritual is a set of actions performed mainly for their symbolic value, that may be prescribed by the traditions of a community.

Religious belief is a strong belief in a supernatural power or powers that control human destiny.
A religious experience is usually an uncommon occurrence in which an individual encounters what he or she considers to be the divine.
Cult refers to a religious movement or group whose beliefs or practices are considered abnormal or bizarre.
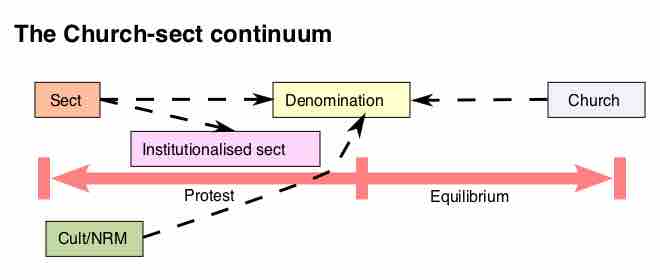
A sect is a group with distinctive religious, political, or philosophical beliefs.

The Christian Church is the assembly of followers of Jesus Christ; in Christianity, a church is the building where its members meet.

Ecclesias are different from churches because they typically must compete with other religious voices in a community.

A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion that operates under a common name, tradition, and identity.

Due to the First Amendment, which grants freedom of religion, there is a diversity of religious beliefs and practices in the U.S.

Religion in the United States is characterized by both a wide diversity in religious beliefs and practices and by a high adherence level.

Christianity is the largest religion in the United States, with around 77% of the population identifying itself as Christian.

Ecumenism mainly refers to initiatives aimed at creating greater Christian unity or cooperation.

Religion plays a "very important" role in the lives of most Americans; a proportion unique among developed nations.

Most modern Western societies are recognized as secular because they enjoy near-complete freedom of religion.

Protestantism is one of the major umbrella religions in the U.S., and is constantly evolving in response to political and social changes.

Catholicism has a long history in the U.S., with the Catholic Church the single largest religious denomination in the United States.

Judaism is the religion, philosophy, and way of life of the Jewish people.

The American Muslim population is a racially diverse group that has been present in the U.S. since before the Civil War.
There are correlations between the degree of religious belief in society and social factors like mortality rates, wealth and happiness.

The main religious preferences in the Unites States include (in order): Christianity, unaffiliate, Judaism, Islam, Buddhism, and Hinduism.

