Chapter 19
Health and Illness
By Boundless
Illness, sometimes considered another word for disease, refers to a state of poor health.
Disparities in health services play out based on different systems of stratification, such as gender.
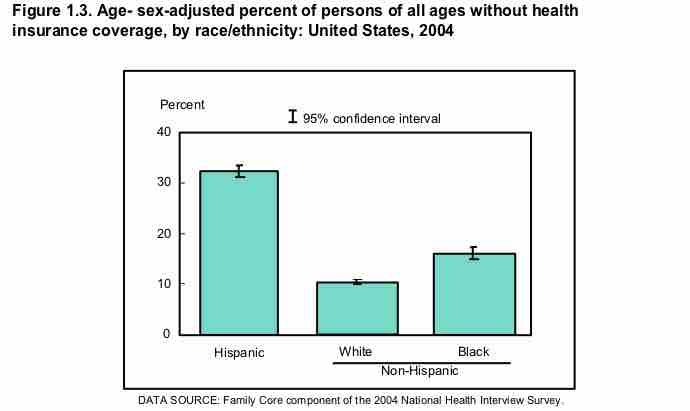
Health disparities refer to gaps in the quality of health and healthcare across racial and ethnic groups.
Social class has a significant impact on one's physical health, ability to receive adequate medical care and nutrition, and life expectancy.

Health literacy is an individual's ability to read, understand and use healthcare information to make decisions about treatment.

Historically and in many parts of the world, women's participation in the profession of medicine has been significantly restricted.

In the functionalist model, Parsons argued that illness is a form of deviance that disturbs the social function of a society.

Conflict theory argues that the economic and political structures of a society create social divisions, inequalities, and conflicts.
According to theorists working in the symbolic interactionist perspective, health and illness are socially constructed.

The labeling approach to health and illness claims that mental illness is manifested solely as a result of societal influence.
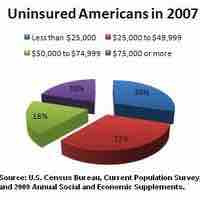
Healthcare in the United States is provided by separate legal entities, often private facilities with governmental insurance for citizens.
The interactions between physicians, nurses, and patients are central to healthcare.

Alternative medicine is any practice claiming to heal "that does not fall within the realm of conventional medicine".
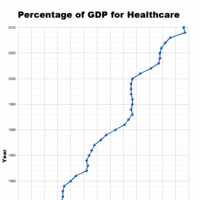
Publicly funded health care is a form of healthcare financing designed to meet the cost of healthcare needs from a publicly managed fund.
European colonization contributed to the spread of disease worldwide.
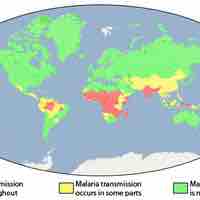
Infectious diseases result from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism.

HIV/AIDS is a major health problem in many parts of the world.
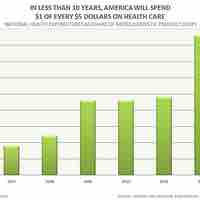
Health insurance is insurance against the risk of incurring personal medical expenses.
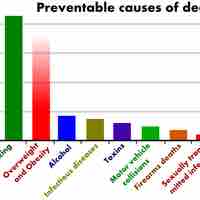
Preventive medicine, or preventive care, refers to measures taken to prevent diseases, rather than curing them or treating their symptoms.