Chapter 16
Economy
By Boundless

In the most simple of terms, economies consist of producing goods and exchanging them; they are fundamentally social systems.
Capitalism is a system that includes private ownership of the means of production, creation of goods for profit, competitive markets, etc.
Karl Marx saw capitalism as a progressive historical stage that would eventually be followed by socialism.

Socialism is an economic system in which the means of production are socially owned and used to meet human needs, not to create profits.

Critiques of socialism generally refer to its lack of efficiency and feasibility, as well as the political/social effects of such a system.

Democratic socialism combines the political philosophy of democracy with the economic philosophy of socialism.

The informal economy consists of economic activity that is neither taxed nor regulated by a government.
Welfare capitalism refers to a welfare state in a capitalist economic system or to businesses providing welfare-like services to employees.

Pre-industrial typically have predominantly agricultural economies and limited production, division of labor, and class variation.

During the Industrial Revolution (roughly 1750 to 1850) changes in technology had a profound effect on social and economic conditions.
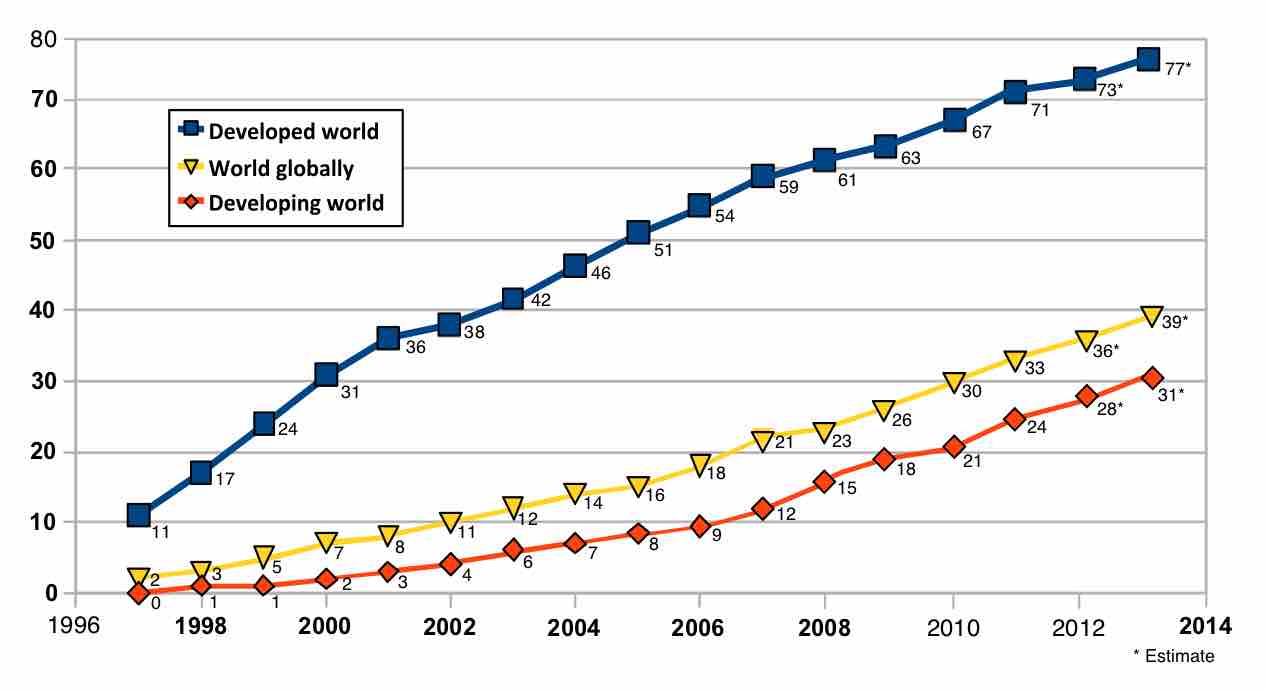
In the "Information Age," individuals can transfer and have instant access to information, leading to a profound economic transformation.

Some thinkers argue that in the last few decades trends associated with globalization have increased the mobility of people and capital.

Global trade (exchange across international borders) has increased with better transportation and governments adopting free trade.

Microfinance is usually understood as the provision of financial services to micro-entrepreneurs and small businesses.

Industry has become more information driven and less labor intensive, leading to a polarization between high- and low-skilled jobs.
Deindustrialization occurs when a country or region loses industrial capacity due to relocation or increased efficiency.
Corporations have powerful legal rights, and some have revenues that exceed the revenues of sovereign nations.
Recently, industry has become more information-intensive, which has led to higher productivity but also higher unemployment and inequality.
After WWII, decolonization ended formal colonialism, but economic inequality has given rise to neocolonialism.

A trade bloc is an agreement where regional barriers to trade are reduced or eliminated among the participating states.
Although we usually think of work as paid, unpaid work is equally important to the economy.

Division of labor is the specialization of cooperative labor in specific, circumscribed tasks and roles.
Industrial labor is labor in industry, usually manufacturing, but it may also include service work, such as cleaning or cooking.

Alienation occurs when the worker can only express individuality through a production system that is not collectively, but privately owned.

Industrial sociology examines the effects of industrial organization on workers, and the conflicts that can result.
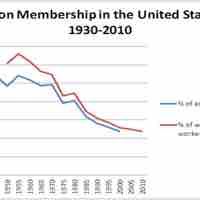
Labor unions provide members with the power of collective bargaining over and fight for workers rights.

The Information Age has impacted the workforce through automation and computerization, resulting in higher productivity and fewer jobs.

Economic sociology is the study of the social causes and social effects of various economic phenomena.