Chapter 7
Deviance, Social Control, and Crime
By Boundless
Deviance refers to behaviors that violate social norms.

Norms are social rules of behavior, and a sanction is a form of punishment against violation of different norms.

Social stigma in deviance is the disapproval of a person because they do not fit the require social norms that are given in society.
Advances in technology have resulted in new forms of deviance as well as new forms of control.

Deviance provides society the boundaries to determine acceptable and unacceptable behaviors in society.

Social control theory argues that relationships, commitments, values, and beliefs encourage conformity.

Conformity is the act of matching attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to group norms.

Informal social control refers to the reactions of individuals and groups that bring about conformity to norms and laws.
Formal means of social control are generally state-determined, through the creation of laws and their enforcement.

Sociological theories of deviance are those that use social context and social pressures to explain deviance.

A biological theory of deviance proposes that an individual deviates from social norms largely because of their biological makeup.

Psychological theories of deviance use a deviant's psychology to explain his motivation or compulsion to violate social norms.

Functionalism claims that deviance help to create social stability by presenting explanations of non-normative and normative behaviors.
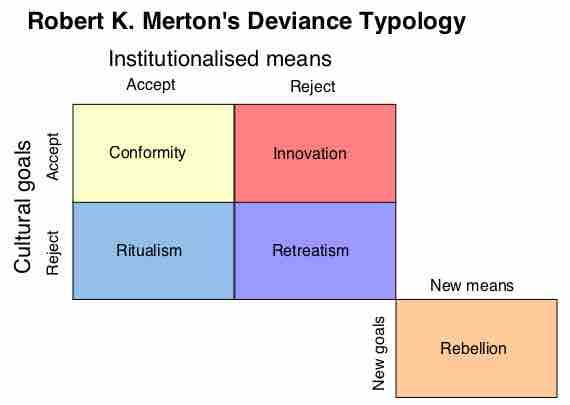
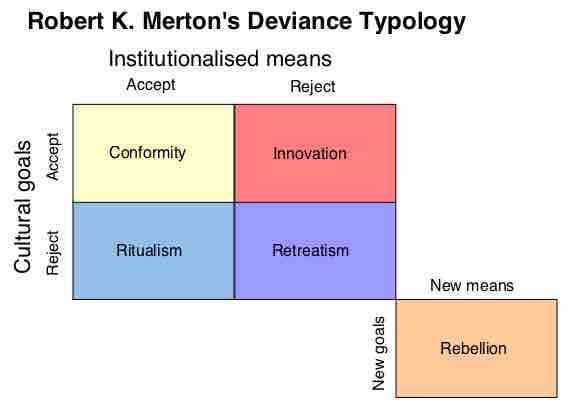
Strain theory states that social structures within society may pressure citizens to commit crimes.

Illegitimate opportunity structures are the rules that operate within deviant subcultures.

Conflict theories emphasize the social, political, or material inequality of a social group, that critique the broad socio-political system.

Class structure within the criminal justice system helps determine the types of crimes individuals will commit.
Power and inequality determine the socioeconomic conditions of different classes.

Oppression is the exercise of authority or power in a burdensome, cruel, or unjust manner.

Differential association is when individuals base their behaviors by association and interaction with others.
Control theory explains that societal institutions without strong control of society can result in deviant behavior.
Labeling theory holds that deviance is not inherent to an act, but instead the result of the externally-imposed label of "deviant".
Crime is the breach of rules or laws for which some governing authority can ultimately prescribe a conviction.

Criminal law, as opposed to civil law, is the body of law that relates to crime and that defines conduct that is not allowed.

Crime statistics attempt to provide statistical measures of the crime in societies.

Juvenile delinquency is participation in illegal behaviors by minors. A juvenile delinquent is typically under the age of 18.

A violent crime is a crime in which the offender uses or threatens to use violent force upon the victim.

Property crime only involves the taking of money or property, and does not involve force or threat of force against a victim.

White-collar crime is a financially motivated, nonviolent crime committed for illegal monetary gain.

Organized crime refers to transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals.

The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by the state to enforce the law, protect property, and limit civil disorder.

A court is a form of tribunal with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties, and carry out the administration of justice.

A prison is a place in which people are physically confined and, usually, deprived of a range of personal freedoms.

Capital punishment is a legal process whereby a person is put to death by the state as a punishment for a crime.