Chapter 3
Culture
By Boundless

Culture relates to nature (our biology and genetics) and nurture (our environment and surroundings that also shape our identities).

Culture is what differentiates one group or society from the next; different societies have different cultures.

A cultural universal is an element, pattern, trait, or institution that is common to all human cultures worldwide.

Culture shock is the personal disorientation a person may feel when experiencing an unfamiliar way of life in a new country.

Ethnocentrism, in contrast to cultural relativism, is the tendency to look at the world primarily from the perspective of one's own culture.
In the social sciences, material culture is a term that refers to the relationship between artifacts and social relations.
Non-material culture includes the behaviors, ideas, norms, values, and beliefs that contribute to a society's overall culture.

The symbolic systems that people use to capture and communicate their experiences form the basis of shared cultures.

The origin of language is a widely discussed and controversial topic due to very limited empirical evidence.

Language may refer either to the human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such.

Various theories assume that language is not simply a representational tool; rather it fundamentally shapes our perception.

Language is a symbolic system of communication based on a complex system of rules relating spoken, signed, or written symbols.

A gesture is a form of non-verbal communication in which visible bodily actions communicate particular messages.
Cultures have values that are largely shared by their members, which identify what should be judged as good or evil.

Social norms are the explicit or implicit rules specifying what behaviors are acceptable within a society or group.

As opposed to forms of internal control, like norms and values, sociologists consider sanctions a form of external control.

Folkways and mores are informal norms that dictate behavior; however, the violation of mores carries heavier consequences.

Culture is a central concept in anthropology, encompassing the range of human phenomena that cannot be attributed to genetic inheritance.

The belief that culture can be passed from one person to another means that cultures, although bounded, can change.
The term "cultural lag" refers to the fact that culture takes time to catch up with technological innovations, resulting in social problems.

Animal culture refers to cultural learning in non-human animals through socially transmitted behaviors.

Despite certain consistent values (e.g. individualism, egalitarianism, freedom, democracy), American culture has a variety of expressions.
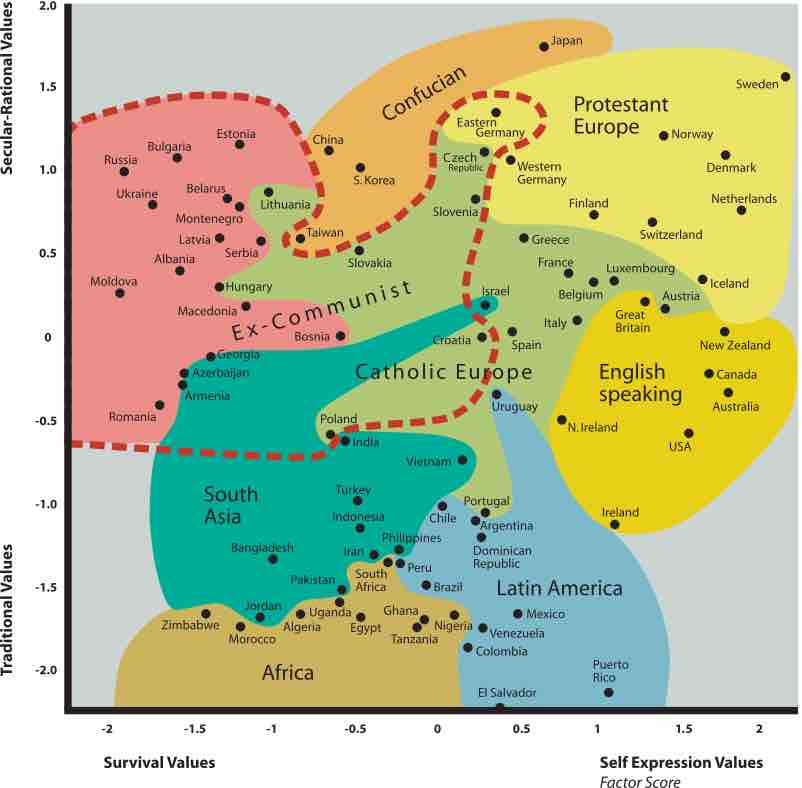
People from different backgrounds tend to have different value systems, which cluster together into a more or less consistent system.

Although various values often reinforce one another, these clusters of values may also include values that contradict one another.

Values tend to change over time, and the dominant values in a country might shift as that country undergoes economic and social change.
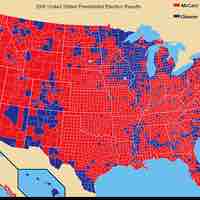
In American usage, "culture war" refers to the claim that there is a conflict between those conservative and liberal values.

Cultures hold values that are largely shared by their members, thereby binding members together.

Any given culture contains a set of values that determine what is important to the society; these values can be idealized or realized.

