Chapter 15
Personality
By Boundless

Personality is the unique combination of patterns that influence behavior, thought, motivation, and emotion in a human being.
The biological perspective on personality emphasizes the influence of the brain and genetic factors on personality.

Both culture and gender are important factors that influence the development of personality.
Allport's, Cattell's, and Eysenck's trait theories propose that individuals possess certain personality traits that partially determine their behavior.
The five-factor model organizes all personality traits along a continuum of five factors: openness, extraversion, conscientiousness, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
While trait theories are useful in categorizing behavior, they have been criticized by a number of psychologists.
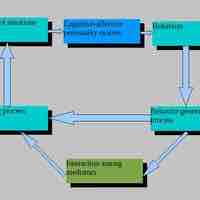
Mischel's cognitive-affective personality theory countered earlier trait theories and resulted in the person–situation debate.
Bandura's and Rotter's social-cognitive theories of personality emphasize cognitive processes, such as thinking and judging.
Critics of the social-cognitive theory of personality argue that it is not a unified theory and does not explain development over time.

According to Freud's psychoanalytic theory, personality develops through a series of stages, each characterized by a certain internal psychological conflict.

Neo-Freudian approaches to the study of personality both expanded on and countered Freud's original theories.
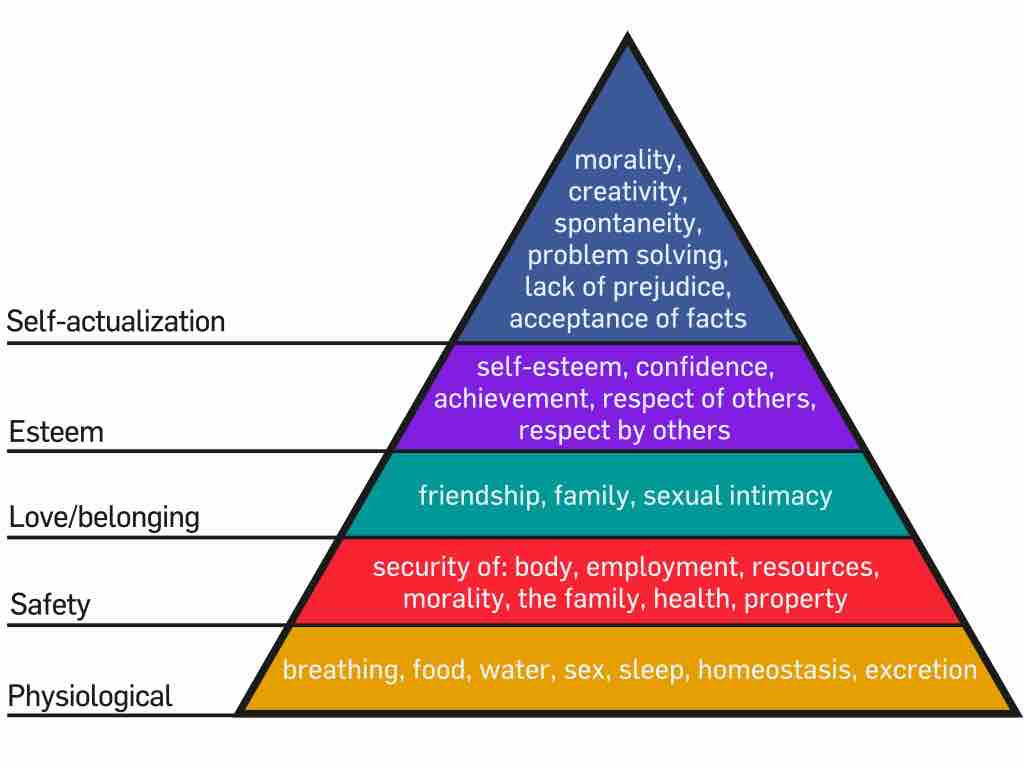
Maslow's humanistic theory of personality states that people achieve their full potential by moving from basic needs to self-actualization.

Carl Rogers' humanistic personality theory emphasizes the importance of the self-actualizing tendency in forming a self-concept.
Psychologists measure personality through objective tests (such as self-reports) and projective measures.

Personality assessments vary in their levels of validity and reliability.
Using personality tests as hiring or evaluation tools in the workplace is very controversial.