Chapter 3
Biological Foundations of Psychology
By Boundless
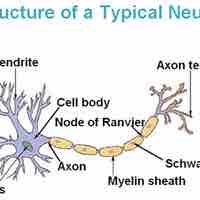
Neurons are specialized cells that transmit chemical and electrical signals to facilitate communication between the brain and the body.
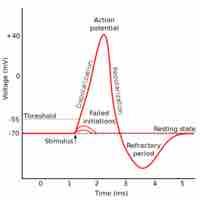
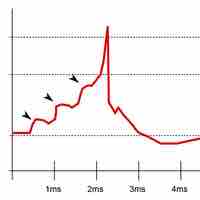
Neural impulses occur when a stimulus depolarizes a cell membrane, prompting an action potential which sends an "all or nothing" signal.
The synapse is the site at which a chemical or electrical exchange occurs between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells.
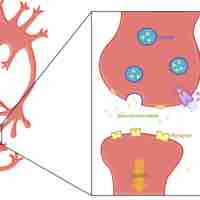
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron across a synapse to a target cell.
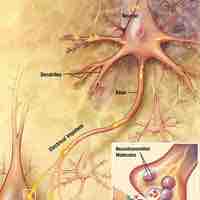
Neural networks consist of a series of interconnected neurons, and serve as the interface for neurons to communicate with each other.
The mental processes and behaviors studied by psychology are directly controlled by the brain, one of the most complex systems in nature.

The brain's lower-level structures consist of the brain stem, the spinal cord, and the cerebellum.
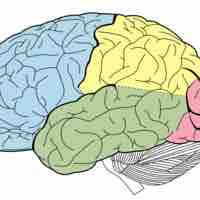
The cerebral cortex is the outermost layered structure of the brain and controls higher brain functions such as information processing.
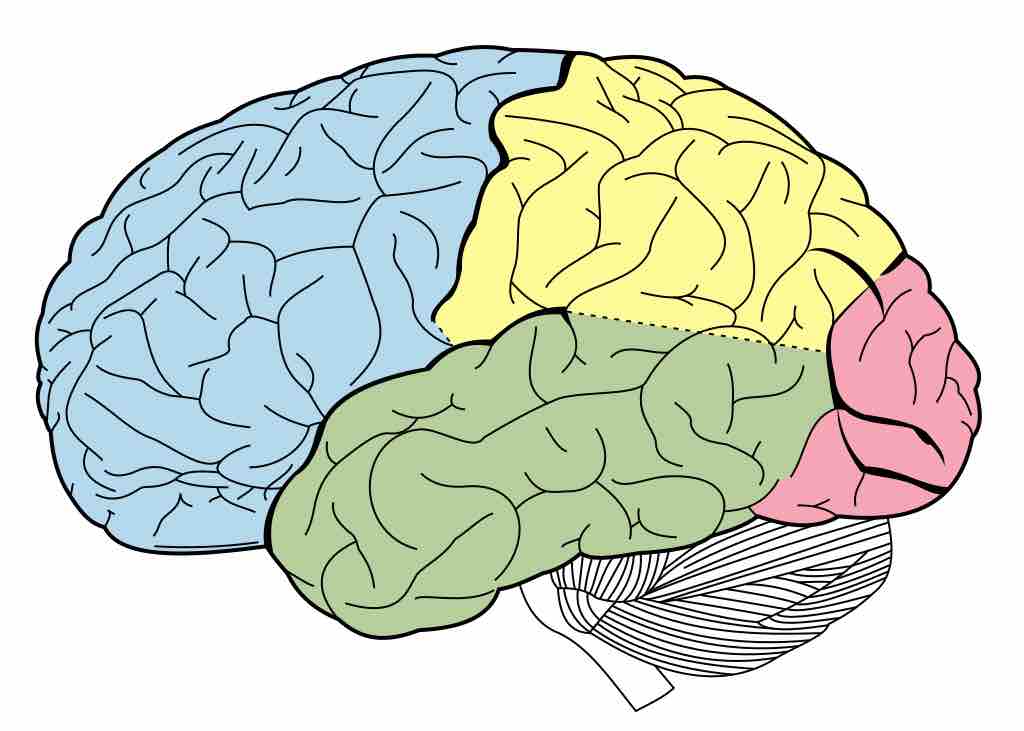
The brain is divided into two hemispheres and four lobes, each of which specializes in a different function.
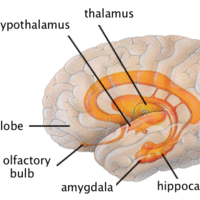
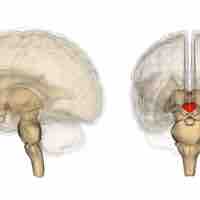
The limbic system combines higher mental functions and primitive emotion into one system.
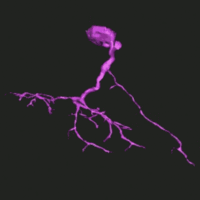
Neuroplasticity is the brain's ability to create new neural pathways to account for learning and acquisition of new experiences.
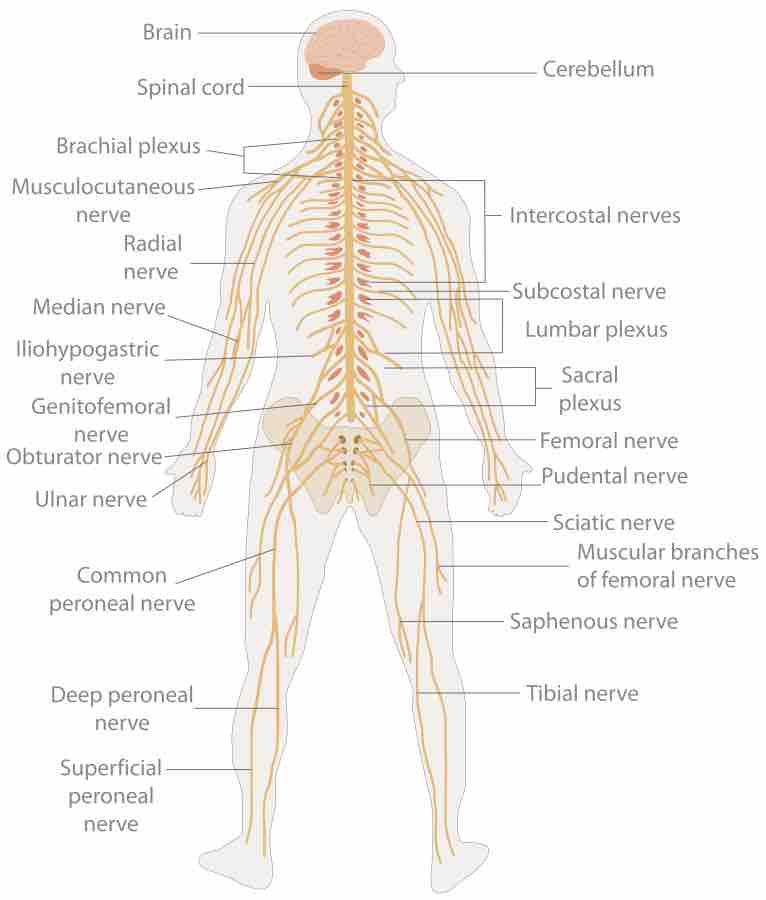
The nervous system controls bodily function by gathering sensory input, integrating that information internally, and communicating proper motor output.
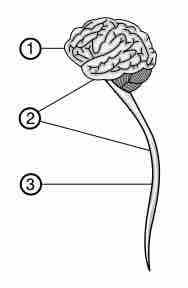
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord, which process sensory input and provide instructions to the body.

The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to environmental stimuli to gather sensory input and create motor output.

The endocrine and nervous systems work together to act as a communication system for the human body.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulates stress in vertebrates.
Hunger is divided into long-term and short-term regulation, each stimulating different hormone responses from the hypothalamus.
Chromosomes contain genetic material that can determine a person's characteristics.
Genetic expression can be influenced by various social factors, as well as environmental factors, from light and temperature to exposure to chemicals.

Genetic makeup has a large role in determining human behavior.
Behavior can influence genetic expression in humans and animals by activating or deactivating genes.