Concept
Version 15
Created by Boundless
Peripheral Motor Endings
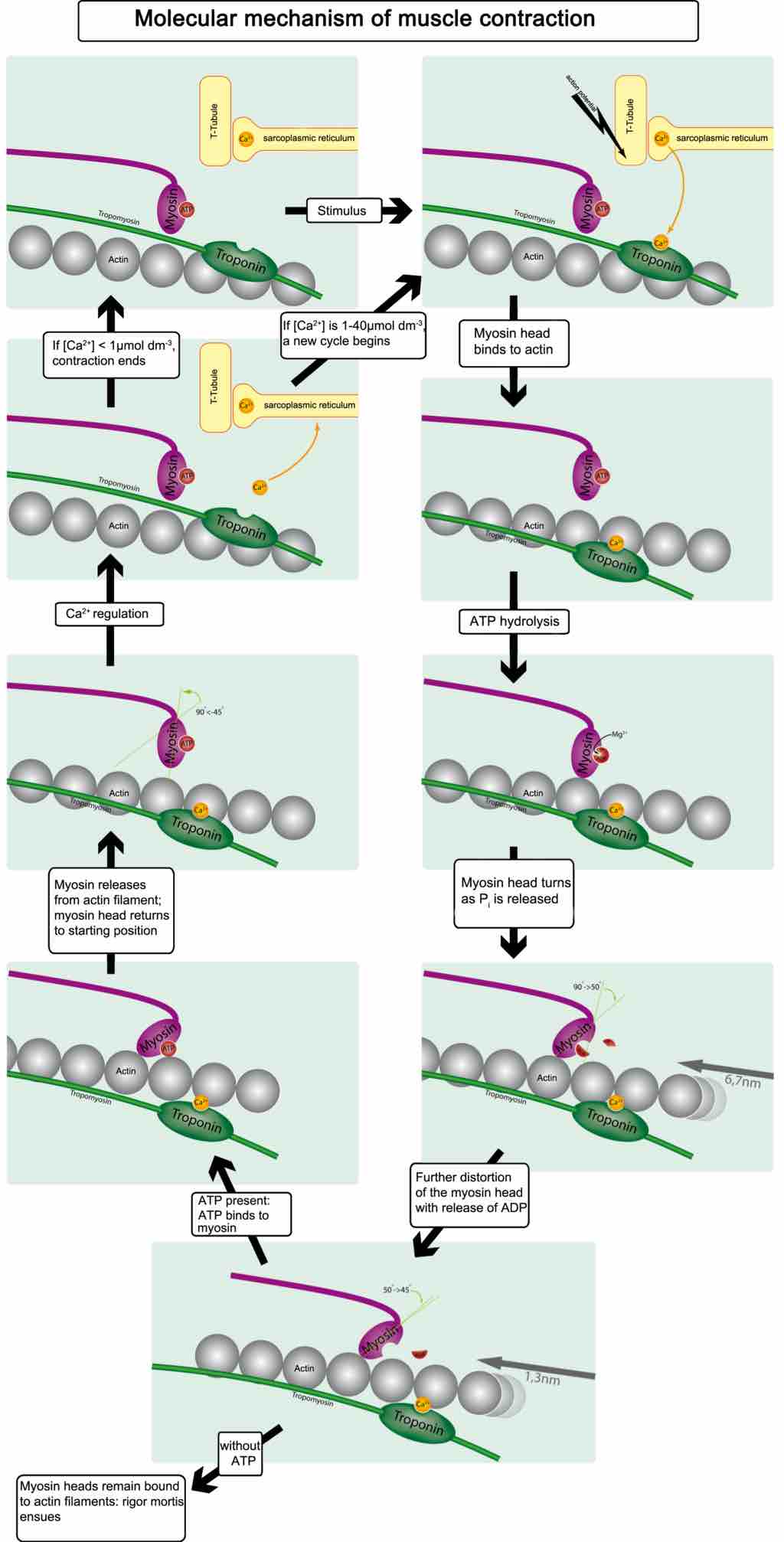
Figure 3. Muscle contraction and actin–myosin interactions
Skeletal muscle contracts following activation by an action potential. The binding of acetylcholine at the motor end plate leads to intracellular calcium release and interactions between myofibrils to elicit contraction.
This diagram shows how muscular contraction is caused at the molecular level. A skeletal muscle contracts following activation by an action potential. The binding of acetylcholine at the motor end plate leads to intracellular calcium release and interactions between myofibrils to elicit contraction.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"Muskel-molekulartranslation."
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Muskel-molekulartranslation.png
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA.