Section 5
Neurophysiology
By Boundless
When a neuron is stimulated, an electrical impulse is generated and conducted along the length of its axon. This process, called action potential, underlies many nervous system functions.

Ion channels are membrane proteins that allow ions to travel into or out of a cell.
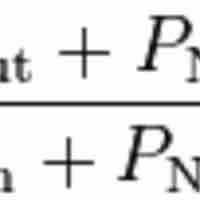
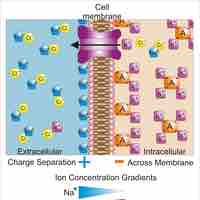
The potential difference in a resting neuron is called the resting membrane potential.
The membrane potential allows a cell to function as a battery, providing electrical power to activities within the cell and between cells.
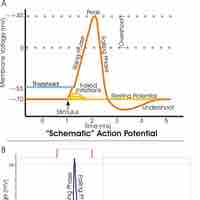
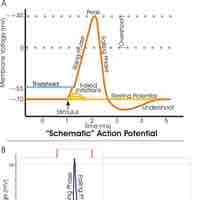
Neurons typically send signals over long distances by generating and propagating action potentials over excitable axonal membrane.

A synapse is a structural junction that mediates information transfer from one neuron to the next or from one neuron to an effector cell as in muscle or gland.
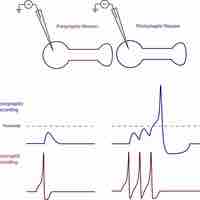
Postsynaptic potentials are excitatory or inhibitory changes in the graded membrane potential in the postsynaptic terminal of a chemical synapse.
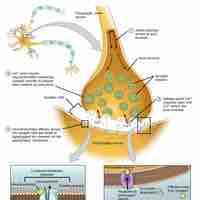
Synaptic transmission is a chemical event which is involved in the transmission of the impulse via release, diffusion, receptor binding of neurotransmitter molecules and unidirectional communication between neurons.
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse.
Although both ionotropic and metabotropic receptors are activated by neurotransmitters, ionotropic receptors are channel-linked while metabotropic receptors initiate a cascade of molecules via G-proteins.
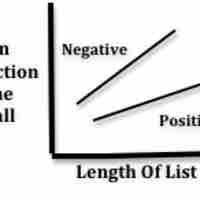
Serial memory processing compares a memory to a target stimulus, while parallel processing carries out multiple operations simultaneously.