The sebaceous glands are microscopic glands found in the skin of mammals . They secrete an oily substance called sebum that is made of fat (lipids) and the debris of dead fat-producing cells. Sebum acts to protect and waterproof hair and skin, and keep them from becoming dry, brittle, and cracked. It can also inhibit the growth of microorganisms on skin.
Sebaceous Gland
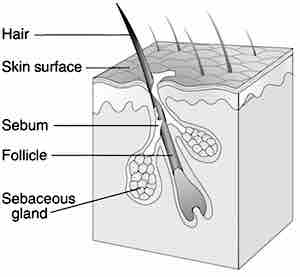
Schematic view of a hair follicle with sebaceous gland.
These glands exist in humans throughout the skin except in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. They are found in greatest abundance on the face and scalp. Sebum is the cause of some people experiencing "oily" hair if it is not washed for several days. In the eyelids, meibomian sebaceous glands secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Mucopurulent discharge is the dry substance accumulating in the corners of the eye after sleeping.
Sebaceous glands can usually be found in hair-covered areas where they are connected to hair follicles to deposit sebum on the hairs, and bring it to the skin surface along the hair shaft. The structure consisting of hair, hair follicle, and sebaceous gland is also known as pilosebaceous unit. Sebaceous glands are also found in non-haired areas of lips, eyelids, penis, labia minora, and nipples; here the sebum reaches the surface through ducts. In the glands, sebum is produced within specialized cells and is released as these cells burst; sebaceous glands are thus classified as holocrine glands.
Sebaceous glands secrete the oily, waxy substance called sebum that is made of triglyceride oils, wax, squalene, and metabolytes of fat-producing cells. In the glands, sebum is produced within specialized cells and is released as these cells burst; sebaceous glands are thus classified as holocrine glands. Seborrhoea is the name for the condition of greasy skin caused by excess sebum.
Sebum is odorless, but its bacterial breakdown can produce odors. Sebum is the cause of some people's experiencing "oily" hair, as in hot weather or if not washed for several days. Earwax is partly composed of sebum.