Chapter 11
Central Nervous System
By Boundless
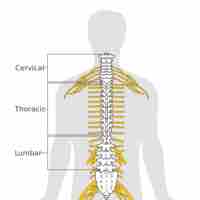
The spinal cord runs along the inside of the vertebral column and serves as the signaling conduit between the brain and the periphery.
The spine encases the spinal cord for protection and support.

The grey matter of the spinal cord contains neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, axons, and nerve synapeses.
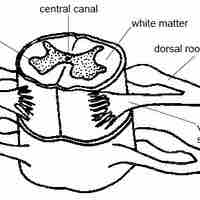
The white matter of the spinal cord is composed of bundles of myelinated axons.
Tight junctions present in the blood-brain barrier separate circulating blood from cerebrospinal fluid, regulating diffusion into the brain.
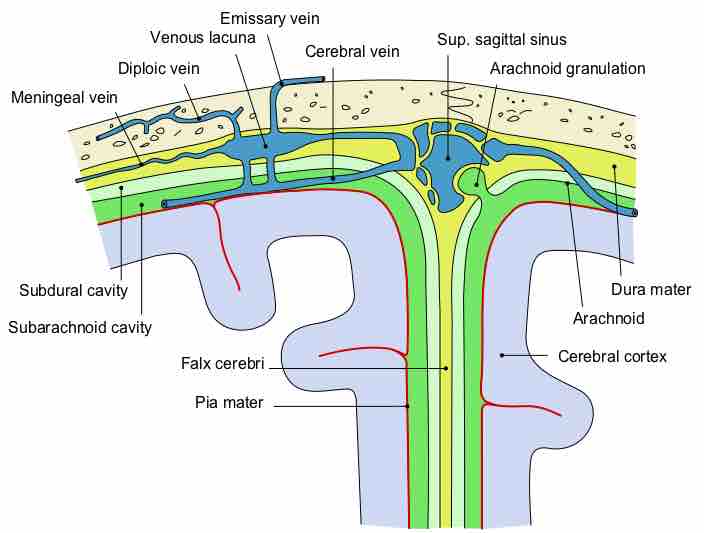
Cerebrospinal fluid is a clear fluid that acts as a cushion for the brain and maintains overall central nervous system homeostasis.

The ventricular system is a set of hollow cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
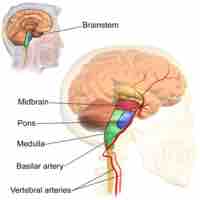
The brainstem regulates vital cardiac and respiratory functions and acts as a vehicle for sensory information.
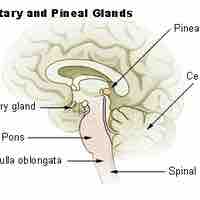
The medulla oblongata controls autonomic functions and connects the higher levels of the brain to the spinal cord.
The pons is a relay station between the forebrain and cerebellum that passes sensory information from the periphery to the thalamus.
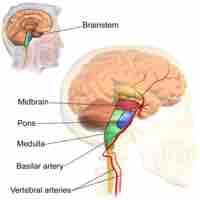
The midbrain plays a major role in both wakefulness and regulation of homeostasis.
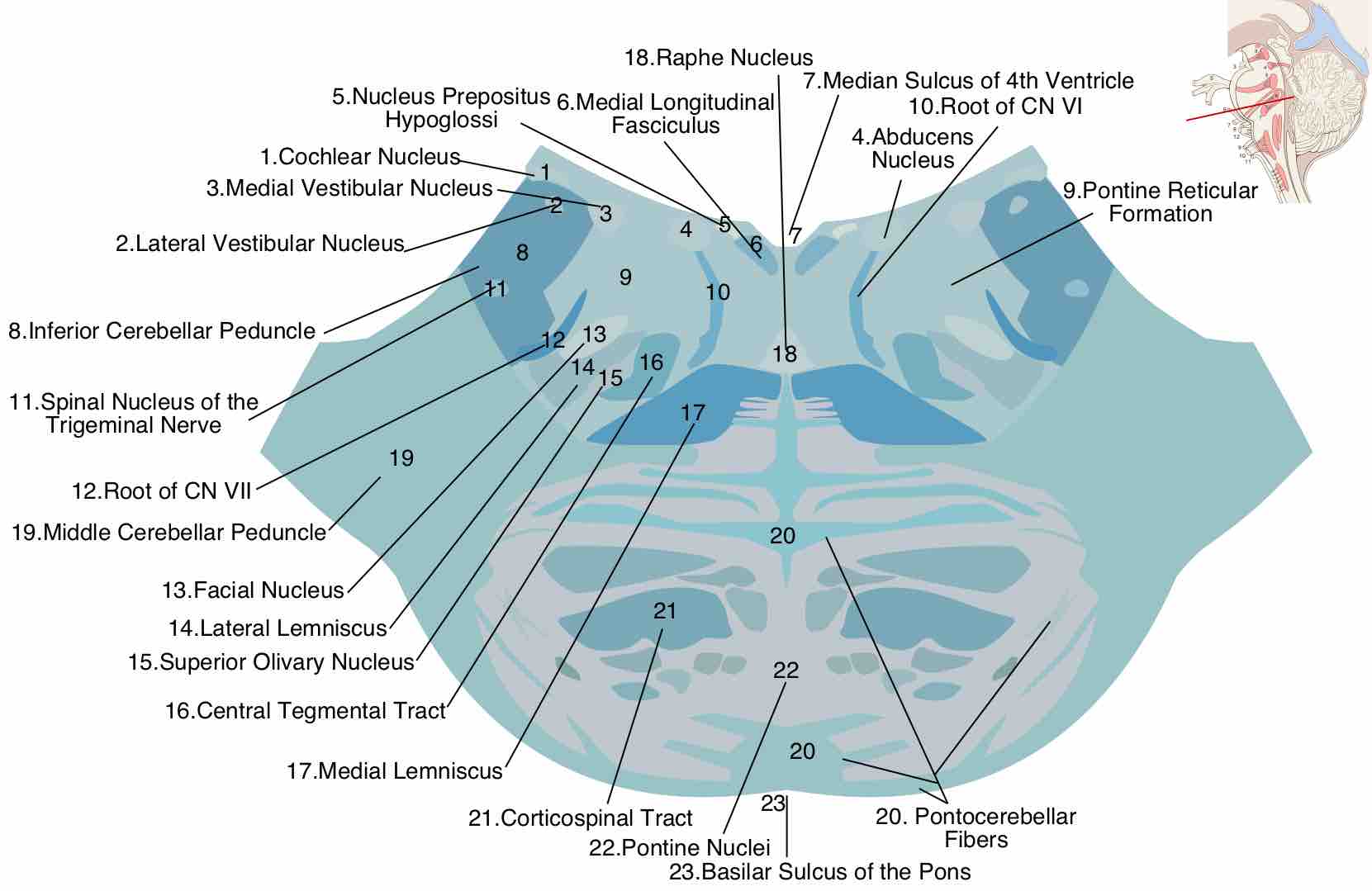
The reticular formation assists in regulation of the sleep cycle and detecting sensory salience.
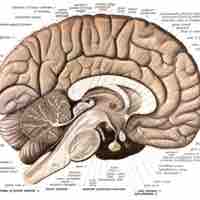
The cerebellum, which looks like a separate structure attached to the bottom of the brain, plays an important role in motor control.
Cerebellar function was once believed to be motor-specific, but newer findings suggest the cerebellum is also involved in higher-level brain processing.
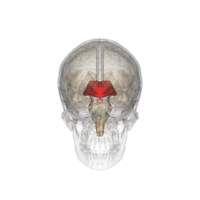
Distinct parts of diencephalon perform numerous vital functions, from regulating wakefulness to controlling the autonomic nervous system.
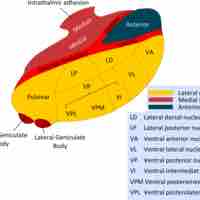
The thalamus is a small structure in the center of the brain that acts as a relay center for sensory and motor information.
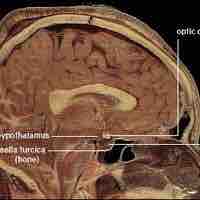
The hypothalamus serves as a gateway between the nervous system and endocrine system.

The epithalamus connects the limbic system to other parts of the brain.
Circumventricular organs are situated adjacent to the brain ventricles and sense concentrations of various compounds in the blood.

With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the body.
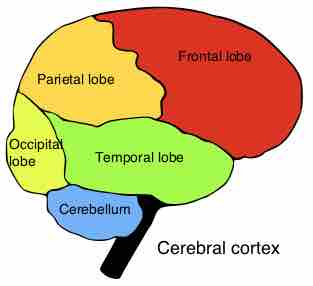
The cortex is divided into four main lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal.
White matter is composed of myelinated axons and glia and connects distinct areas of the cortex.
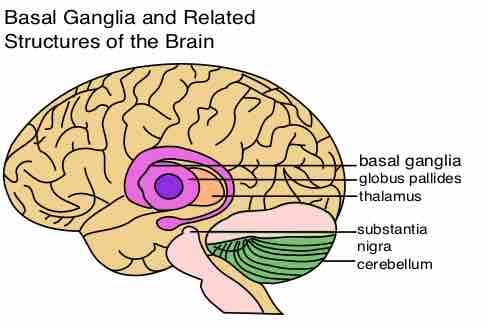
The basal ganglia is important for initiating planned movements and forming habits, both referred to as 'behavior selection' or 'switching'.

The limbic system makes up the inner border of the cortex and is vital for emotion, motivation, and memory.
Sensory areas of the brain receive and process sensory information, including sight, touch, taste, smell, and hearing.
The motor areas, arranged like a pair of headphones across both cortex hemispheres, are involved in the control of voluntary movements.
Associative areas of the cortex integrate current states with past states to predict proper responses based on sets of stimuli.

The human brain is composed of a right and a left hemisphere, and each participates in different aspects of brain function.
- Introduction to the Nervous System
- Neuroglia
- Neurons
- Collections of Nervous Tissue
- Neurophysiology