Muscular or distributing arteries are medium-sized arteries that draw blood from an elastic artery and branch into resistance vessels, including small arteries and arterioles. In contrast to the mechanism elastic arteries use to store and dissipate energy generated by the heart's contraction, muscular arteries contain layers of smooth muscle providing allowing for involuntary control of vessel caliber and thus control of blood flow. Muscular arteries can be identified by the well-defined elastic lamina that lies between the tunicae intima and media.
The splenic artery (lienal artery), the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen, is an example of a muscular artery. It branches from the celiac artery and follows a course superior to the pancreas. The splenic artery branches off to the stomach and pancreas before reaching the spleen and gives rise to arterioles that directly supply capillaries of these organs.
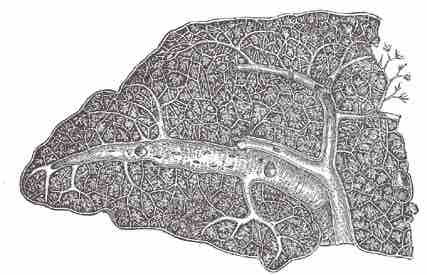
Splenic Artery
Transverse section of the human spleen showing the distribution of the splenic artery and its branches