Chapter 16
Cardiovascular System: Blood
By Boundless
Blood is composed of plasma and three types of cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Blood contains plasma and blood cells, some of which have hemoglobin that makes blood red. The average blood volume in adult is five liters.
The main function of blood is to supply oxygen to tissues and remove carbon dioxide. Other functions include pH regulation and thermoregulation.
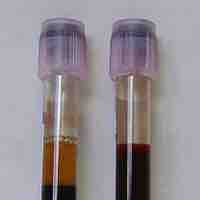
Plasma comprises about 55% of total blood volume. It contains proteins and clotting factors, transports nutrients, and removes waste.
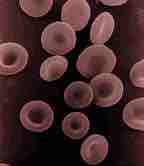
Red blood cells lack nuclei and have a biconcave shape.
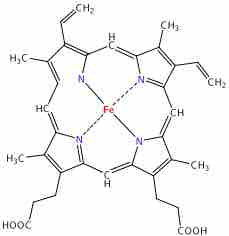
The primary functions of red blood cells (RBCs) include carrying oxygen to all parts of the body, binding to hemoglobin, and removing carbon dioxide.
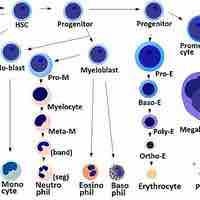
Human erythrocytes are produced through a process called erythropoiesis. They take about seven days to mature.
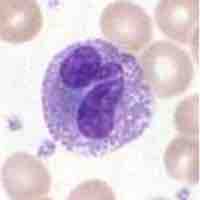
The different types of white blood cells (leukocytes) include neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages.
Each of the several types of white blood cells provide a specific major function in defending the body against infections.
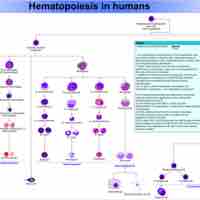
Haematopoiesis refers to the formation of blood cells components. It is necessary for vertebrate function.
Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occurs.
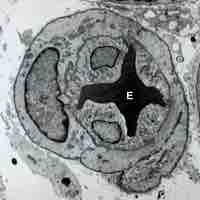
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels, which reduces blood loss during injury.
At the site of vessel injury, platelets stick together to create a plug, which is the beginning of blood clot formation.

Coagulation is the process by which a blood clot forms to reduce blood loss after damage to a blood vessel.

Vitamin K is an essential factor of the coagulation cascade.
Clot retraction is the shrinking of a blood clot facilitated by thrombolytic agents.

Fibrinolysis is a process of breaking down clots in order to prevent them from growing and becoming problematic.
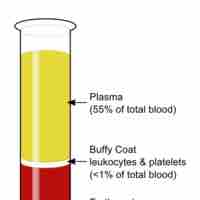
Whole blood refers to human blood transfusion from a standard blood donation.
A volume expander is a type of intravenous therapy that provides fluid replacement for the circulatory system.
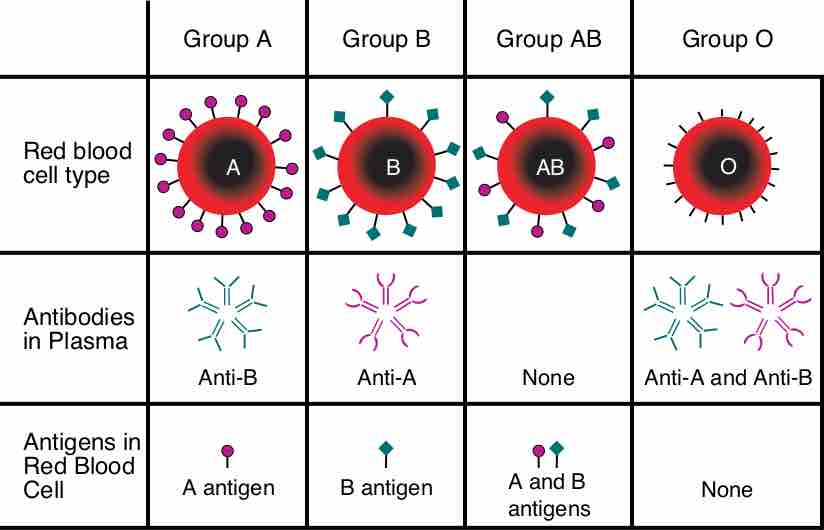
Red blood cells have surface-expressed proteins that define the self/not-self nature of the cells.
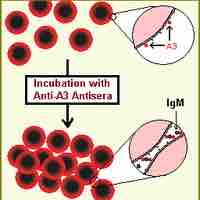
Blood banks test donor blood to ensure recipient compatibility, reducing the risk of hemolytic reaction, renal failure, and death.