Section 4
Acid-Base Balance
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
4 concepts
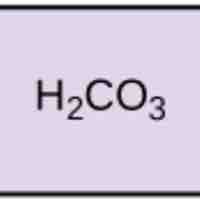
pH, Buffers, Acids, and Bases
Acids dissociate into H+ and lower pH, while bases dissociate into OH- and raise pH; buffers can absorb these excess ions to maintain pH.

Chemical Buffer Systems
Chemical buffers such as bicarbonate and ammonia help keep blood pH in the narrow range compatible with life.
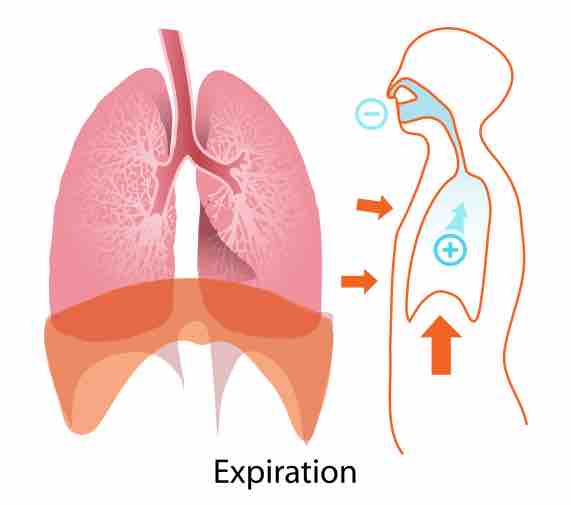
Regulation of H+ by the Lungs
Acid-base imbalances in blood pH can be altered by changes in breathing to expel more CO2, which will raise pH back to normal.
The Role of the Kidneys in Acid-Base Balance
The kidneys help maintain acid-base balance by excreting hydrogen ions into the urine and reabsorbing bicarbonate from the urine.