Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also referred to as motor neuron disease in British English, is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. The condition is sometimes called Lou Gehrig's disease in the U.S., after the New York Yankees baseball player who was diagnosed with the disease in 1939. The disorder is characterized by rapidly progressive weakness, muscle atrophy and fasciculations, muscle spasticity, difficulty speaking (dysarthria), difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and decline in breathing ability.
Symptoms of ALS
The disorder causes muscle weakness and atrophy throughout the body as a result of degeneration of the upper and lower motor neurons. Unable to function, the muscles weaken and atrophy. Affected individuals may ultimately lose the ability to initiate and control all voluntary movement, although bladder and bowel sphincters and the muscles responsible for eye movement are usually, but not always, spared. Cognitive function is generally spared for most patients although some (~5%) also have frontotemporal dementia. A higher proportion of patients (~30%–50%) also have more subtle cognitive changes that may go unnoticed but are revealed by detailed neuropsychological testing. Sensory nerves and the autonomic nervous system are generally unaffected meaning the majority of people with ALS will maintain sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste. Bladder and bowel functions are also rarely affected by ALS.
The earliest symptoms of ALS are typically obvious weakness and/or muscle atrophy. Other presenting symptoms include muscle fasciculation (twitching), cramping, or stiffness of affected muscles; muscle weakness affecting an arm or a leg; and/or slurred and nasal speech. The parts of the body affected by early symptoms of ALS depend on which motor neurons in the body are damaged first. About 75% of people contracting the disease experience "limb onset" ALS (i.e., first symptoms in the arms or legs). Patients with the leg onset form may experience awkwardness when walking or running or notice that they are tripping or stumbling, often with a "dropped foot" which drags gently along the ground. Arm-onset patients may experience difficulty with tasks requiring manual dexterity such as buttoning a shirt, writing, or turning a key in a lock. Occasionally, the symptoms remain confined to one limb for a long period of time or for the whole length of the illness; this is known as monomelic amyotrophy.
Over time, patients experience increasing difficulty moving, swallowing (dysphagia), and speaking or forming words (dysarthria). Symptoms of upper motor neuron involvement include tight and stiff muscles (spasticity) and exaggerated reflexes (hyperreflexia) including an overactive gag reflex. Symptoms of lower motor neuron degeneration include muscle weakness and atrophy, muscle cramps, and fleeting twitches of muscles that can be seen under the skin (fasciculations). To be diagnosed with ALS, patients must have signs and symptoms of both upper and lower motor neuron damage that cannot be attributed to other causes.
Difficulty swallowing and chewing making eating normally very difficult and increase the risk of choking or aspirating food into the lungs. In later stages of the disease, aspiration pneumonia and maintaining a healthy weight can become a significant problem and may require insertion of a feeding tube. As the diaphragm and intercostal muscles (rib cage) that support breathing weaken, measures of lung function such as forced vital capacity and inspiratory pressure diminish. In respiratory onset ALS, this may occur before significant limb weakness is apparent. Most people with ALS die of respiratory failure or pneumonia. The median survival time from onset to death is around 39 months, and only 4% survive longer than 10 years. The best-known person with ALS, Stephen Hawking, has lived with the disease for more than 40 years, though his is an unusual case.
Causes and Treatments of ALS
For patients without a family history of the disease, which includes ~95% of cases, there is no known cause for ALS. Potential causes for which there is inconclusive evidence includes head trauma, military service, and participation in elite sports. Many other potential causes including chemical exposure, electromagnetic field exposure, occupation, physical trauma, and electric shock have been investigated but without consistent findings.
Riluzole (Rilutek) as of 2011 is the only treatment that has been found to improve survival, but only to a modest extent. It lengthens survival by several months, and may have a greater survival benefit for those with a bulbar onset. It also extends the time before a person needs ventilation support. Other treatments for ALS are designed to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients. This supportive care is best provided by multidisciplinary teams of health care professionals working with patients and caregivers to keep patients as mobile and comfortable as possible.
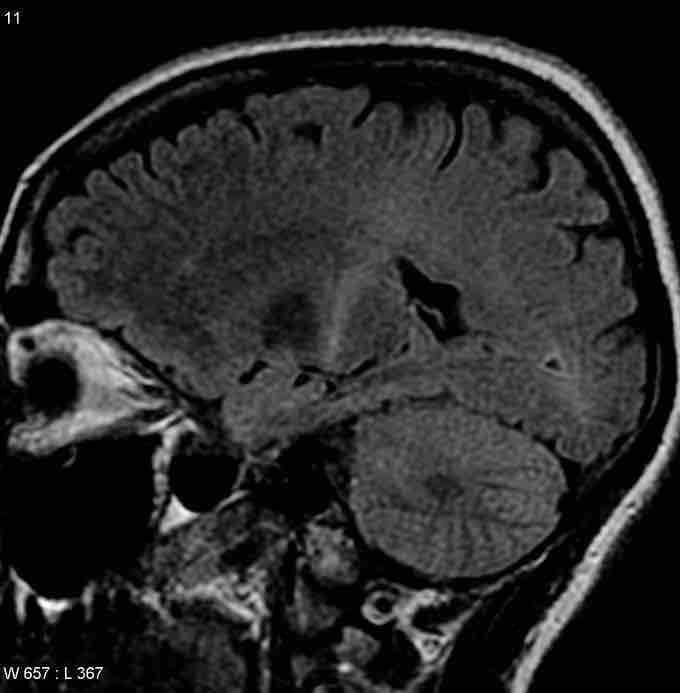
Coronal MRI of an ALS patient
MRI (parasagittal FLAIR) demonstrates increased T2 signal within the posterior part of the internal capsule and can be tracked to the subcortical white matter of the motor cortex, outlining the corticospinal tract), consistent with the clinical diagnosis of ALS.