Overview
Although vectors and scalars represent different types of physical quantities, it is sometimes necessary for them to interact. While adding a scalar to a vector is impossible because of their different dimensions in space, it is possible to multiply a vector by a scalar. A scalar, however, cannot be multiplied by a vector.
To multiply a vector by a scalar, simply multiply the similar components, that is, the vector's magnitude by the scalar's magnitude. This will result in a new vector with the same direction but the product of the two magnitudes.
Example
For example, if you have a vector A with a certain magnitude and direction, multiplying it by a scalar a with magnitude 0.5 will give a new vector with a magnitude of half the original. Similarly if you take the number 3 which is a pure and unit-less scalar and multiply it to a vector, you get a version of the original vector which is 3 times as long. As a more physical example take the gravitational force on an object. The force is a vector with its magnitude depending on the scalar known as mass and its direction being down. If the mass of the object is doubled, the force of gravity is doubled as well .
Multiplying vectors by scalars is very useful in physics. Most of the units used in vector quantities are intrinsically scalars multiplied by the vector. For example, the unit of meters per second used in velocity, which is a vector, is made up of two scalars, which are magnitudes: the scalar of length in meters and the scalar of time in seconds. In order to make this conversion from magnitudes to velocity, one must multiply the unit vector in a particular direction by these scalars.
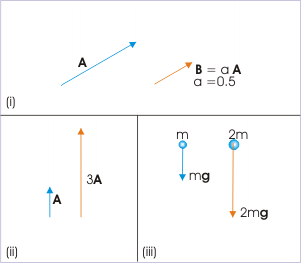
Scalar Multiplication
(i) Multiplying the vector