Concept
Version 10
Created by Boundless
A Microscopic View: Drift Speed
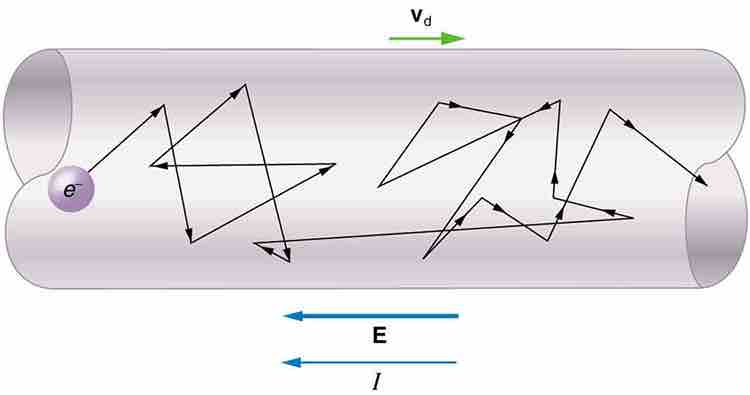
Drift Speed
Free electrons moving in a conductor make many collisions with other electrons and atoms. The path of one electron is shown. The average velocity of the free charges is called the drift velocity and is in the direction opposite to the electric field for electrons. The collisions normally transfer energy to the conductor, requiring a constant supply of energy to maintain a steady current.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"OpenStax College, College Physics. October 26, 2012."
http://cnx.org/content/m42341/latest/?collection=col11406/1.7
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.