As mRNAs are transcribed a phenomenon of "stuck" or stalled ribosomes can occur. Stuck mRNA transcripts can arise from many different mechanisms such as premature 3' adenylation or cryptic polyadenylation signals within the coding region of a gene. This lack of a stop codon results a significant issue for cells. Ribosomes translating the mRNA eventually translate into the 3'poly-A tail region of transcripts and stalls. As a result it cannot eject the mRNA. Ribosomes thus may become sequestered associated with the nonstop mRNA and would not be available to translate other mRNA molecules into proteins.
There are two ways in which cells deal with stuck ribosomes, nonstop mediated decay (NSD) and Trans-translation. Nonstop mediated decay mediates this problem by both freeing the stalled ribosomes and marking the nonstop mRNA for degradation in the cell by nucleases. Nonstop mediated decay consists of destroying the nonstop mRNA. The first pathway proteins bind to the stuck ribosome. This binding allows the ribosome to eject the stuck mRNA molecule – this even frees the ribosome and allows it to translate other transcripts. The proteins which freed the ribosome remain with the mRNA which targets the nonstop mRNA for recognition by RNA degradation pathway. NSD is best understood in eukaryotes but similar processes occur in bacteria.
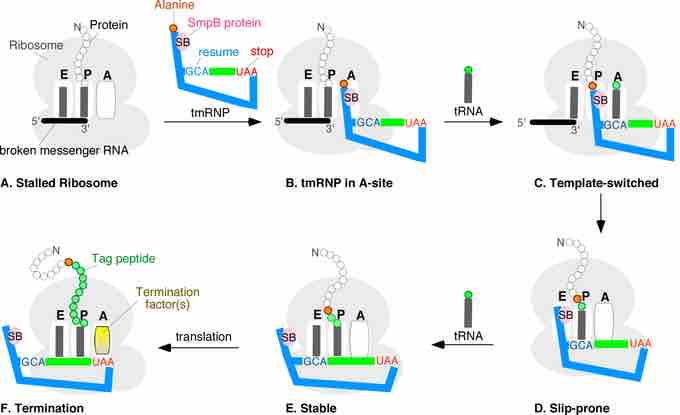
Trans-translation is a recently discovered pathway in E. coli, although it is not completely understood, it involves Transfer-messenger RNA (abbreviated tmRNA) which is a bacterial RNA molecule with dual tRNA-like and messenger RNA-like properties. It is generally agreed that tmRNA first occupies the empty A site of the stalled ribosome. Subsequently, the ribosome moves from the 3' end of the truncated messenger RNA onto the tmRNA where it translates the codons of the tmRNA until the tmRNA stop codon is encountered. Depending on the organism, the resulting truncated protein is degraded and the truncated mRNA . Trans-translation is essential in some bacterial species, whereas other bacteria require tmRNA to survive when subjected to stressful growth conditions.
Trans-translation
rans-Translation stages A through F. A ribosome with its RNA binding sites, designated E, P, and A, is stuck near the 3' end of a broken mRNA. The tmRNP binds to the A-site, allowing the ribosome to switch templates from the broken message onto the open reading frame of the tmRNA via the resume codon (blue GCA). Regular translation eventually resumes. Upon reaching the tmRNA stop codon (red UAA), a hybrid protein with a proteolysis tag (green beads) is released.