Small regulatory RNAs encompass a specific class of RNAs that affect gene regulation. These RNAs are typically small non-coding RNA molecules that are highly structured and are comprised of numerous stem-loops. These small regulatory RNAs play a critical role in gene regulation via numerous mechanisms. The mechanisms by which small regulatory RNAs function include binding to protein targets, protein modification, binding to mRNA targets, and regulating gene expression . There are numerous classes of small regulatory RNAs that play a key role in regulation.
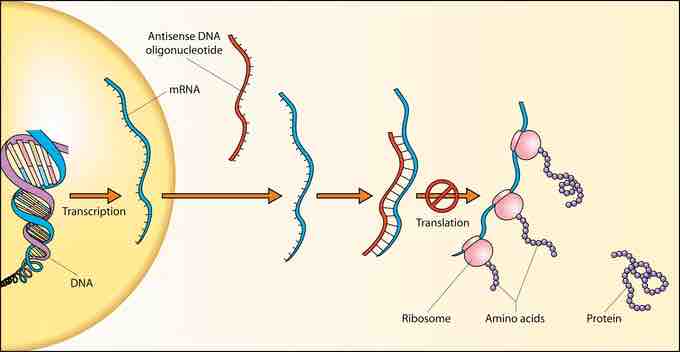
Overview of Antisense DNA
This image displays a mechanism of antisense DNA. However, it is important to note that an antisense RNA functions in the same manner. The antisense RNA can bind to the mRNA and inhibit translation. In some cases, small regulatory RNAs, not included in the antisense category, can activate translation as well.
Antisense RNAs
Antisense RNAs are used to bind to complementary mRNAs and inhibit protein translation. Antisense RNAs are single stranded RNAs that can be utilized as a laboratory technique to inhibit protein translation. Antisense RNAs have also been found to be naturally occurring in bacteria such as E. coli with the R1 plasmid. The antisense RNAs are categorized as small regulatory RNAs due to their small size. They can be divided into either cis- or trans-antisense RNAs. Cis-antisense RNAs are encoded by an overlap between the antisense RNA itself and the target gene. In trans-antisense RNAs, the antisense RNA gene is separate from the target gene and there is no overlap.
House-keeping RNAs
Small regulatory RNAs encompass many RNAs involved in house-keeping processes as well. House-keeping genes are specific genes that function in maintaining basic cellular processes and a state of homeostasis. House-keeping RNAs identified to date include rRNA and tRNAs. rRNAs that are considered to be house-keeping genes can bind to RNA polymerases and regulate transcription or function in larger complexes that are required for protein secretion or synthesis processes.
Regulation of RPoS
RPoS genes specifically encode for sigma factors which function as regulators of transcription and stress responses. Small RNAs have been shown to regulate RPoS translation and those identified thus far include: DsrA, RprA, and OxyS. These RNAs can either activate or inhibit RPoS translation.
Outer Membrane Protein Regulation
Small regulatory RNAs have also been identified in regulation of outer membrane proteins that function in critical cellular processes such as controlling entry and exit to the cell. The outer membrane functions as a barrier for the cell and its ability to allow for transport is strictly controlled. For example, the small regulatory RNAs, MicC, and MicF, are able to regulate expression of outer membrane proteins (OmpC and OmpF) which function in controlling transport of metabolites and toxins.