Chapter 11
Immunology
By Boundless
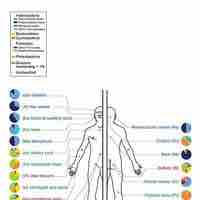
The immune system includes primary lymphoid organs, secondary lymphatic tissues and various cells in the innate and adaptive immune systems.
Human-microbial interactions can be commensal or mutualistic, as with many types of gut flora, or harmful, as with pathogenic bacteria.
The immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease.
Natural killer cells are part of the innate immune response that recognize abnormal MHC I molecules on infected/tumor cells and kill them.
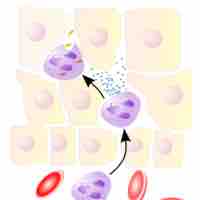
The innate immune response has physical and chemical barriers that exist as the first line of defense against infectious pathogens.
Around 20 soluble proteins comprise the complement system, which helps destroy extracellular microorganisms that have invaded the body.
Upon pathogen entry to the body, the innate immune system uses several mechanisms to destroy the pathogen and any cells it has infected.
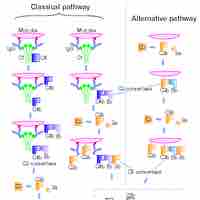
The complement system helps or "complements" the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism.
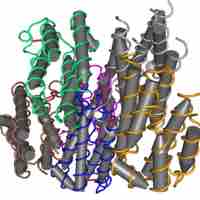
Interferons (IFNs) are proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of pathogens.
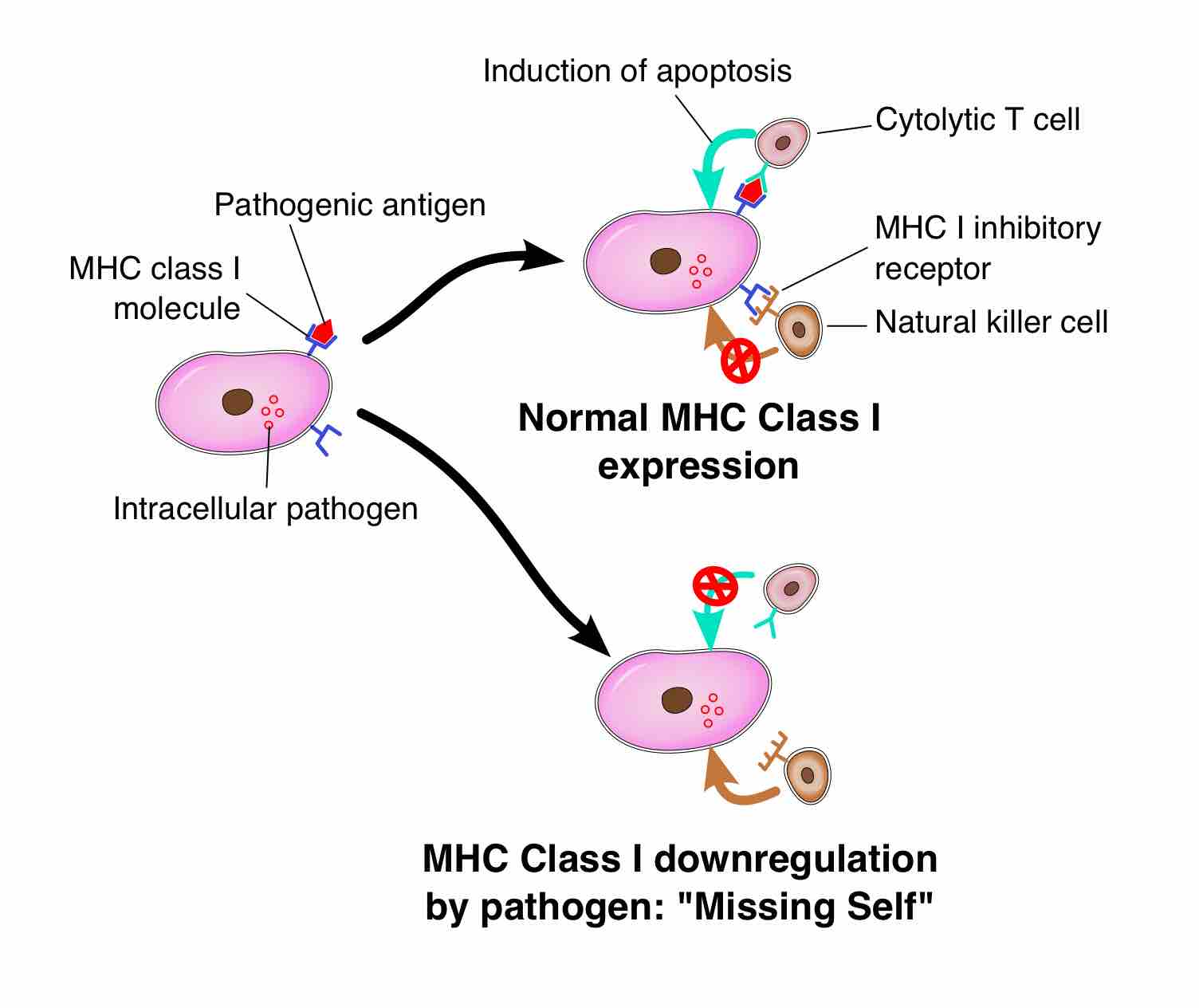
Natural killer cells (or NK cells) are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system.
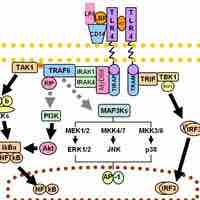
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system as well as the digestive system.
Iron binding proteins of the innate immune system include lactoferrin and transferrins.
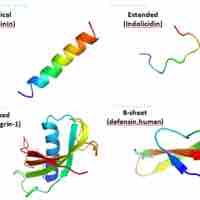
Antimicrobial peptides are an evolutionarily conserved component of the innate immune response and are found among all classes of life.
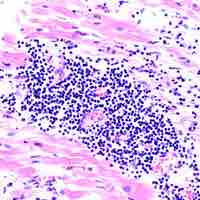
In autoimmune heart diseases, the body's immune defense system mistakes its own cardiac antigens as foreign, and attacks them.
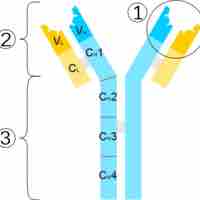
A region at the tip of the antibody protein is very variable, allowing millions of antibodies with different antigen-binding sites to exist.

Complex genetic mechanisms evolved which allow vertebrate B cells to generate a diverse pool of antibodies from relatively few antibody genes.
The clonal selection hypothesis is a widely accepted model for the immune system's response to infection.
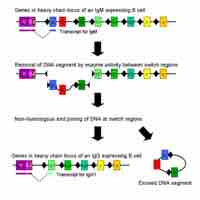
Isotype class switching is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of antibody from one class to another.
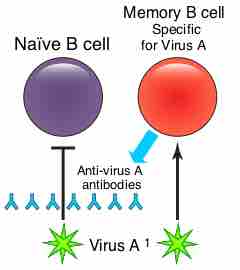
Memory B cells are a B cell sub-type that are formed following primary infection.
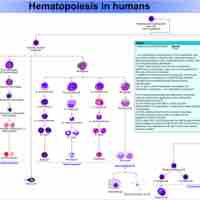
The immune system protects organisms from infection first with the innate immune system, then with adaptive immunity.
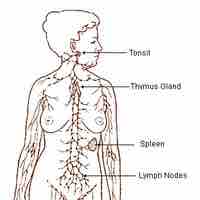
The lymphatic system houses large populations of immune cells which are released upon detection of a pathogen.
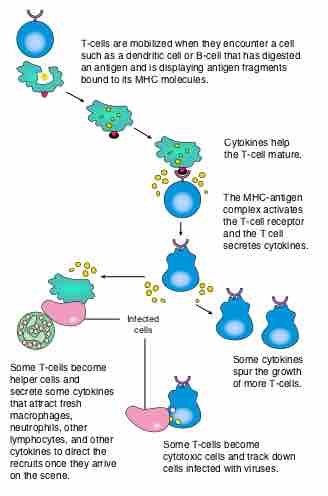
T cells play a central role in cell-mediated immune response through the use of the surface T cell receptor to recognize peptide antigens.
Cell-mediated immunity involves cytotoxic T cells recognizing infected cells and bringing about their destruction.
Regulatory T cells are a subset of T cells which modulate the immune system and keep immune reactions in check.
The T Cell Receptor (TCR) found on the surface of T cells is responsible for recognizing antigens.
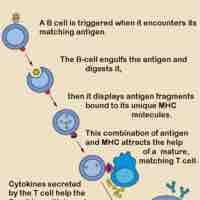
Adaptive immunity is stimulated by exposure to infectious agents and recruits elements of the immunoglobulin superfamily.
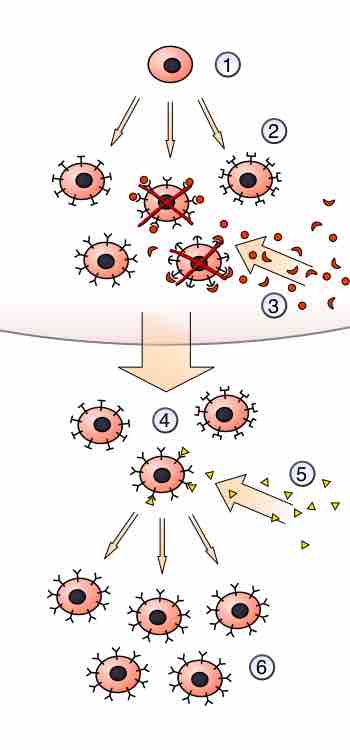
Clonal selection and tolerance select for survival of lymphocytes that will protect the host from foreign antigens.

Cytokines and chemokines are both small proteins secreted by cells of the immune system.

Superantigens are a class of antigens that cause activation of T-cells and massive cytokine release.
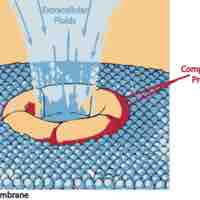
The complement system helps antibodies and phagocytic cells clear pathogens from an organism.
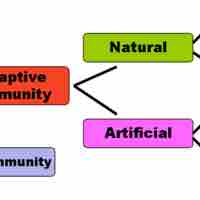
Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when a person is exposed to a live pathogen, develops the disease, and then develops immunity.
Naturally acquired passive immunity occurs during pregnancy, when antibodies are passed from the maternal blood into the fetal bloodstream.
Artificial immunity is a mean by which the body is given immunity to a disease by intentional exposure to small quantities of it.