Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney tissue, calyces, and renal pelvis. It is commonly caused by bacterial infection that has spread up the urinary tract or travelled through the bloodstream to the kidneys.
A similar term is "pyelitis" which means inflammation of the pelvis and calyces. In other words, pyelitis together with nephritis is collectively known as pyelonephritis. Severe cases of pyelonephritis can lead to pyonephrosis (pus accumulation around the kidney), sepsis (a systemic inflammatory response of the body to infection), kidney failure and even death.
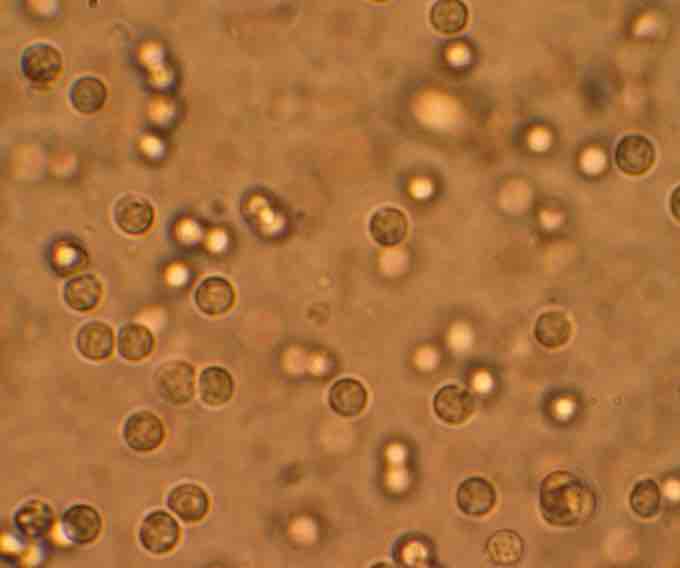
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
White blood cells in the urine of someone with a UTI, seen under a microscope.
Pyelonephritis presents with fever, accelerated heart rate, painful urination, abdominal pain radiating to the back, nausea, and tenderness at the costovertebral angle on the affected side. Pyelonephritis that has progressed to urosepsis may be accompanied by signs of septic shock, including rapid breathing, decreased blood pressure, violent shivering, and occasionally delirium. Pyelonephritis requires antibiotic therapy, and sometimes surgical intervention, as well as treatment of any underlying causes to prevent its recurrence.