Bond Yield Plus Risk Premium Approach
The bond yield plus risk premium (BYPRP) approach is another method we can use to determine the value of an asset, specifically, a company's publicly traded equity. BYPRP allows us to estimate the required return on an equity by adding the equity's risk premium to the yield to maturity on company's long-term debt.
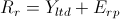
Bond Yield Plus Risk Premium Equation
States that the required return on an equity equals the yield of the company's long-term debt plus the equity's risk premium.
Bond Yield vs. Risk Premium
Simply put, the yield on a bond is the rate of return received from the investment. In the BYPRP approach, we use a bond's yield to maturity, which is the discount rate at which the sum of all future cash flows from the bond (coupon payments and principal payments) are equal to the price of the bond. This is also referred to as the internal rate of return (IRR).
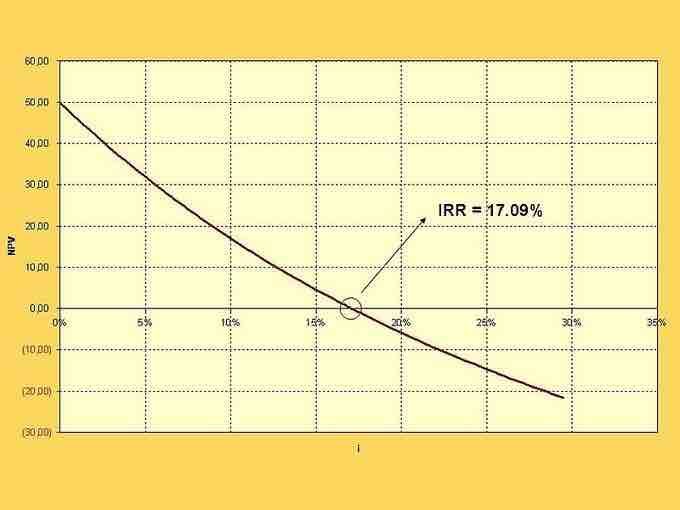
Yield To Maturity Graph
A hypothetical graph showing yield to maturities (or internal rates of return) for corresponding present values.
The equity risk premium is essentially the return that stocks are expected to receive in excess of the risk-free interest rate. The normal historical equity risk premium for all equities has been just over 6%. In general, an equity's risk premium will be between 5% and 7%. Common methods for estimating the equity risk premium include:
- The Fed Model (forward operating earnings yield [earnings per share divided by share price] minus the 10-year U.S. Treasury Bond yield)
- The dividend yield plus projected earnings growth, minus the 10-year Treasury yield
- The historical stock returns minus the 10-year Treasury yield
Estimating the value of an equity using the bond yield plus risk premium approach has its drawbacks. We can only utilize the BYPRP approach if the entity has publicly traded debt, and it does not produce as accurate an estimate as the capital asset pricing model or discounted cash flow analysis.
Moreover, equity risk premium estimates can be highly inaccurate, while also varying wildly depending on which model is used. It can be very difficult to get an accurate estimate of the risk premium on an equity, having a duration of roughly 50 years, using a risk-free rate of such short duration as a 10-year Treasury bond.
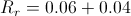
Example Equation
Required return = 6% + 4%