The business cycle is comprised of the upward and downward movement in the level of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) over time . These fluctuations occur around a long-term growth trend, and typically involve shifts over time between periods of relatively rapid economic growth (an expansion or boom), and periods of relative stagnation or decline (a contraction or recession).
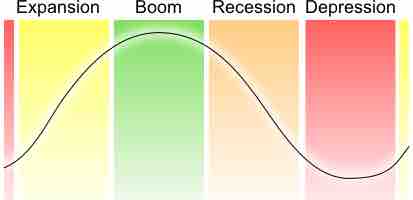
Cycles in the economy
The economy moves through expansion and contraction on a routine basis; policy mechanisms allow for smoother transitions and soften landings.
Policy Responses
When the economy is not at a steady state and instead is at a point of either overheating (growing to fast) or slowing, the government and monetary authorities have policy mechanisms, fiscal and monetary, respectively, at their disposal to help move the economy back to a steady state growth trajectory. If the economy needs to be slowed, these policies are referred to as contractionary and if the economy needs to be stimulated the policy prescription is expansionary.
Expansionary Policy
Expansionary fiscal policy involves government spending exceeding tax revenue, and is usually undertaken during recessions. Fiscal authorities will increase government spending in order to revive the economy.
Expansionary monetary policy relies on the central bank increasing availability of loanable funds through three mechanisms: open market operations, discount rate, and the reserve ratio. As the supply of loanable funds increases, the interest rate is expected to decrease and thereby increase the desire to borrow funds for consumption and investment purposes.
Contractionary Policy
Contractionary fiscal policy is opposite of the action taken in an expansionary purpose, and occurs when government spending is lower than tax revenue.
Similarly, contractionary monetary policy is the opposite of expansionary monetary policy and occurs when the supply of loanable funds is limited, to reduce the access and availability to relatively inexpensive credit.