Imports
Imports are defined as purchases of good or services by a domestic economy from a foreign economy. The domestic purchaser of the good or service is called an importer. Imports and exports are critical for many economies and they are the defining financial transactions of international trade.
Protecting Imports
Due to the economic importance of imports, countries enact specific laws, barriers, and policies in order to regulate international trade. Protectionism is the economic policy of restraining trade between countries through tariffs on imported goods, restrictive quotas, and government regulations. When trade barriers and policies of protectionism are eliminated, consumer surplus increases. The price of a good or service will decrease while the quantity consumed will increase.
Impacts of Buying Imported Goods
On a national level, in most countries international trade and importing goods represents a significant share of the gross domestic product (GDP). International trade has a significant economic, social, and political importance in many countries. Imports provide countries with access to goods and services from other nations. Without imports, a country would be limited to the goods and services within its own borders .
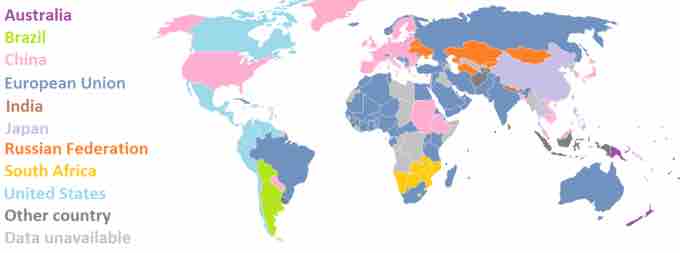
Imports
The map shows the largest importers on an international scale. The color indicates the leading source of merchandise imports for the indicated country (the United States' imports the largest percentage of its goods from China). Imports account for a significant share in the gross domestic product (GDP) of a country.
International trade is generally less expensive than domestic trade despite additionally imposed costs, taxes, and tariffs. However, the factors of production are usually more mobile domestically than internationally (capital and labor). It is common for countries to import goods rather than a factor of production. For example, the U.S. imports labor-intensive goods from China. Instead of importing Chinese labor, the U.S. imports goods that were produced in China by Chinese labor.
On a business level, companies take part in direct-imports, which occur when a major retailer imports goods that are designed locally from an overseas manufacturer. The direct-import program allows the retailer to bypass the local supplier and purchase the final product directly from the manufacturer. Direct imports save retailers money by eliminating the local supplier.