Exports
Export is defined as the act of a country shipping goods and services out of the port of a country. In international trade, an export refers to the selling of goods and services produced in the home country to other markets (other countries) . The seller of the goods and services is referred to as the "exporter. "
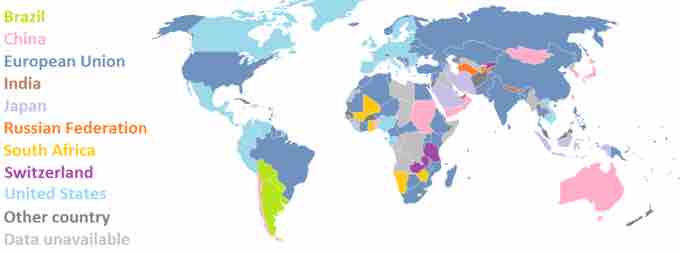
Exports
The map shows the primary exporters for countries around the globe. The colors indicate the leading merchandise export destination for the indicated country (the United States main export destination is the European Union). Exporting is the act of shipping goods and services to other countries.
Protecting Exports
In order to protect exports, commercial goods are subject to customs authorities for both the exporting and importing countries. Legal restrictions and trade barriers are in place internationally to control trade, whether goods are being exported or imported. When legal restrictions and trade barriers are lessened or lifted the producer surplus increases and so does the amount of the goods and services that are exported to other countries.
Impact of Exports
Exporting goods and services has both advantages and disadvantages for countries involved in international trade.
Exporting allows a country's producers to gain ownership advantages and develop low-cost and differentiated products. It is viewed as a low-risk mode of production and trade. Exporters also experience internationalization advantages which are the benefits of retaining a core competence within a company and threading it through the value chain instead of obtaining a license to outsource or sell the goods or services.
Disadvantages of exporting are mainly the result of manufacturers having to sell their goods to importers. In domestic sales, manufacturers sell directly to wholesalers or even directly to the retailer or customer. For exports, manufacturers face and extra layer in the chain of distribution which squeezes the margins. As a result, manufacturers may have to offer lower prices to the importers than to domestic wholesalers in order to move their product and generate business.