Producer surplus is affected by many different factors. Changes in the price level, the demand and supply curves, and price elasticity all influence the total amount of producer surplus, other things held constant.
Changes in Price
Changes in price are directly associated with the amount of surplus a producer will receive. Graphically, the producer surplus is directly above the supply curve, but below the price. Other things equal, as equilibrium price increases, the amount of potential producer surplus and the number of goods supplied increases. Lower prices result in lower potential producer surplus and goods supplied: with a lower equilibrium price, the producer surplus triangle will be smaller.

Economic Surplus
The producer surplus is directly above the supply curve and is shaded in blue.
Demand Curve
Shifts in the demand curve are directly related to the amount of producer surplus. If demand decreases, and the demand curve shifts to the left, producer surplus decreases. Conversely, if demand increases, and the demand curve shifts to the right, producer surplus increases.
At an initial demand represented by the "Demand (1)" curve, producer surplus is the blue triangle made of
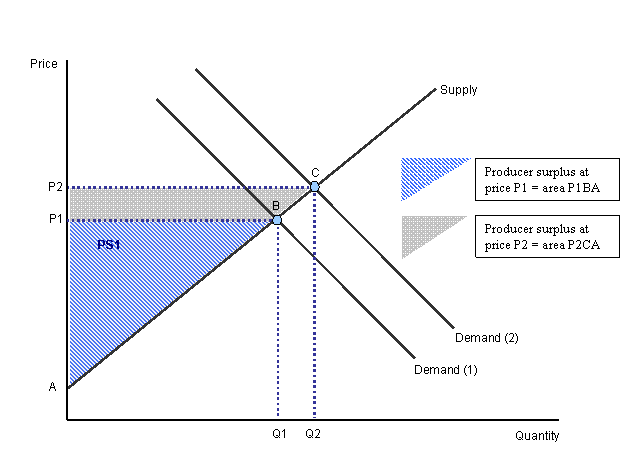
Producer Surplus and the Demand Curve
If the demand curve shifts out, producer surplus increases, as seen by size of the gray triangle.
Supply Curve
Similarly, shifts in the supply curve are also directly related to the amount of potential surplus. Decreases in the supply curve will cause decreases in producer surplus. Increases in the supply curve will cause increases in producer surplus.
At an initial supply represented by the "Supply (1)" curve, producer surplus is the blue triangle made of
Price Elasticity of Supply
Price elasticity of supply is the relationship between price and quantity changes. It measures how quantity supplied is affected by changes in price. When supply is elastic, producers can increase production without much price or cost change. When supply is inelastic, producers cannot change production easily.
When supply is perfectly elastic, it is depicted as a horizontal line. Producer surplus is zero because the price is not flexible. Producers cannot provide a higher price than market price.
When supply is perfectly inelastic, it is depicted as a vertical line. Producer surplus is infinite because the price is completely flexible.