Producer surplus is the difference between what price producers are willing and able to supply a good for and what price they actually receive from consumers. It is the extra money, benefit, and/or utility producers get from selling a product at a price that is higher than their minimum accepted price, as shown by the supply curve.
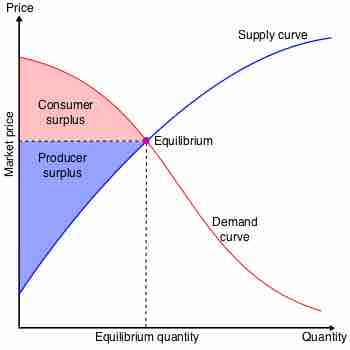
Economic Surplus
Producer surplus is the shaded area directly above the supply curve, up to the equilibrium point. Consumer surplus is the shaded area directly under the demand curve, up to the equilibrium point.
For example, above, the equilibrium price is
Similarly, at
This process is repeated for every price level up to the equilibrium price. To find the resulting total producer surplus, all of the rectangles for the individual price levels are added together, and the total area is the total producer surplus. Below, the total producer surplus is made of all three pink rectangles - the surpluses at price levels of
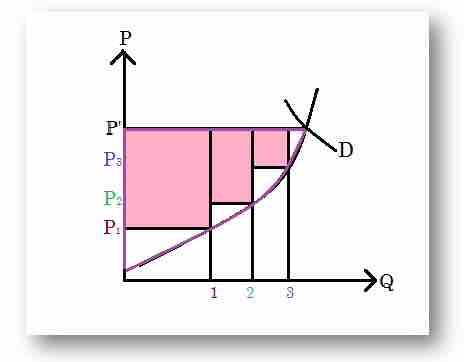
Producer surplus
In the figure, producer surplus at different prices is represented by the pink rectangles.