Chapter 20
Economic Growth
By Boundless

Economic growth is measured as the increase in real gross domestic product (GDP) in the long-run, through higher resources or productivity.
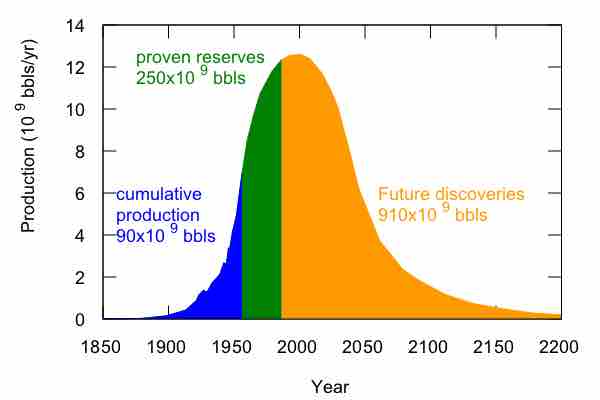
Economies throughout history are defined by an evolution towards common currencies, global trade, and technologies driving productivity.
Economic growth is typically viewed as positive, but there are mixed repercussions of increased productivity within an economic system.
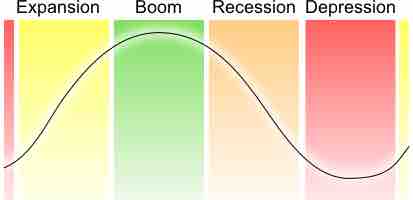
Economic growth is the increase in the market value of goods and services produced by an economy over time; the percentage rate of increase in the GDP.

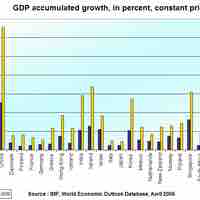
The economy in the United States is the world's largest single national economy; 2013 GDP estimation was $16.6 trillion.

On a global scale, economic growth is the sum of the growth of individual countries to give a worldwide total.

Developing countries can catch up to developed countries by achieving growing faster, which is determined by a wide number of country-specific factors.
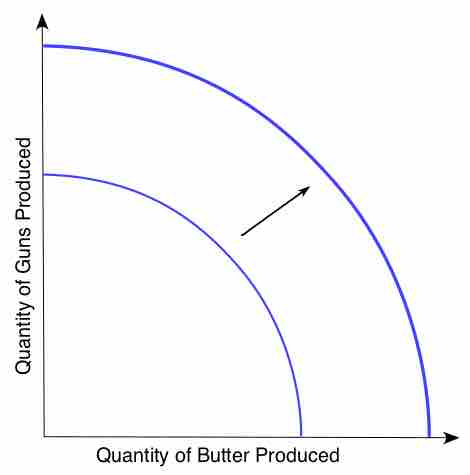
Increasing productivity is a rare win-win, improving the standard of living from a governmental, commercial and consumer perspective.
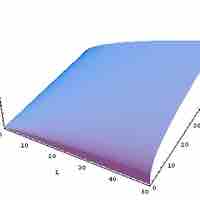
Productivity is represented by production functions, and is the amount of output that can be generated from a set of inputs.
Technological advances play a crucial role in improving productivity, and thus the standard of living in a system.
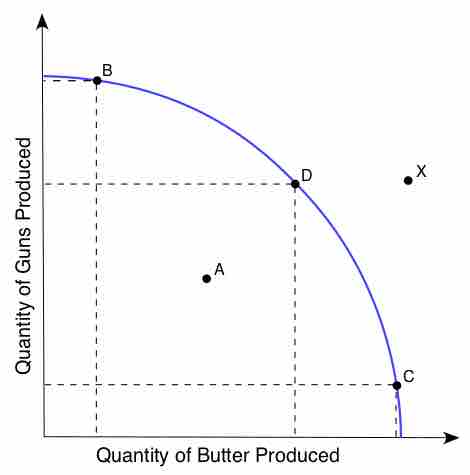
Long-run growth is defined as the sustained rise in the quantity of goods and services that an economy produces.
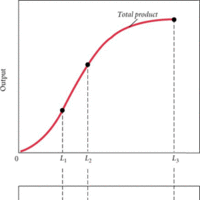
The aggregate production function examines how the productivity depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker.

In economics and long-run growth, worker productivity is influenced directly by fixed capital, human capital, physical capital, and technology.
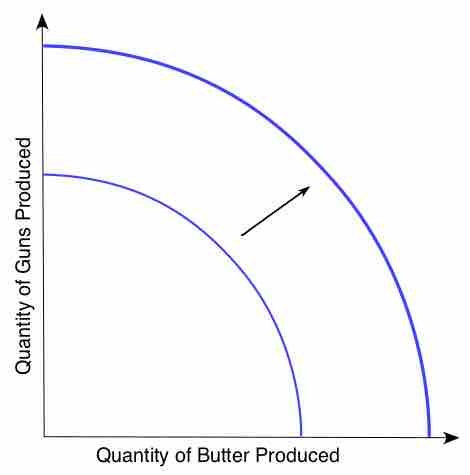
In economics, technological change is a term used to describe the change in a set of feasible production possibilities.
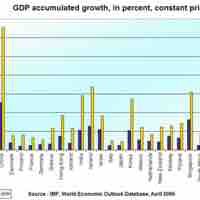
Government activity and policies have a direct impact on long-run growth. It can invest, and operate through monetary and fiscal policy.
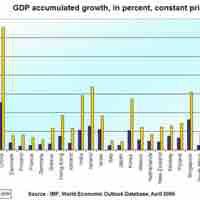
Economic growth has the potential to make all people richer, but may have downsides such as increased inequality and environmental impacts.
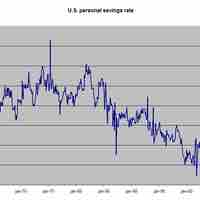
The government can incentivize savings and investment by changing the relative cost of taking each action.
A country can impact its long-term growth by affecting human capital through education and healthcare investments.
Property rights are theoretical constructs that determine how a resource is used and owned.
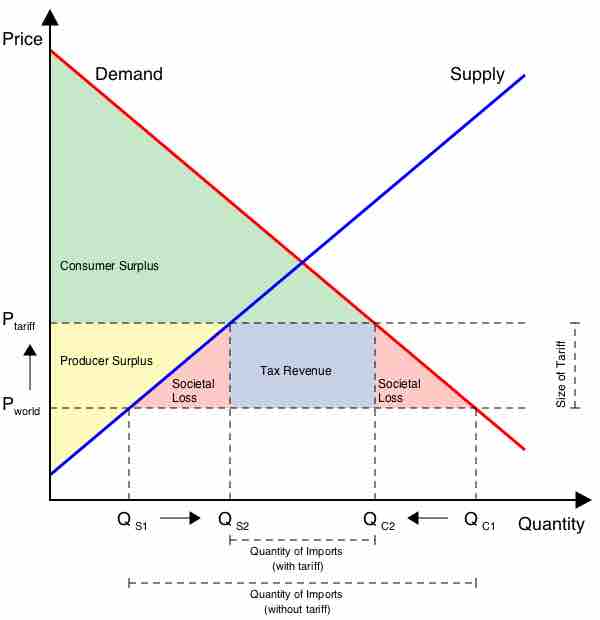
Government can promote free trade by reducing tariffs, quotas, and non-tariff barriers.
The government can establish intellectual property laws, directly conduct research, or finance research and development.