Section 2
Theory of Consumer Choice
By Boundless
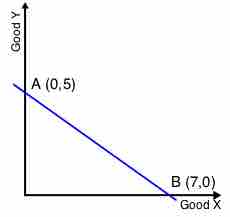
Budget constraints represent the plausible combinations of products and services a buyer can purchase with the available capital on hand.

Economists mapping consumer preferences use indifference curves to illustrate a series of goods that represent equivalent utility.
Almost all indifference curves will be negatively sloped, convex, and will not intersect.
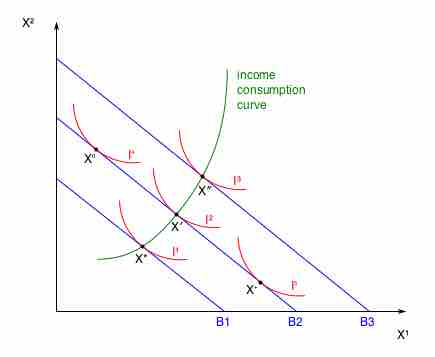
One of the central considerations for a consumer's consumption choice is income or wage levels, and thus their budgetary constraints.
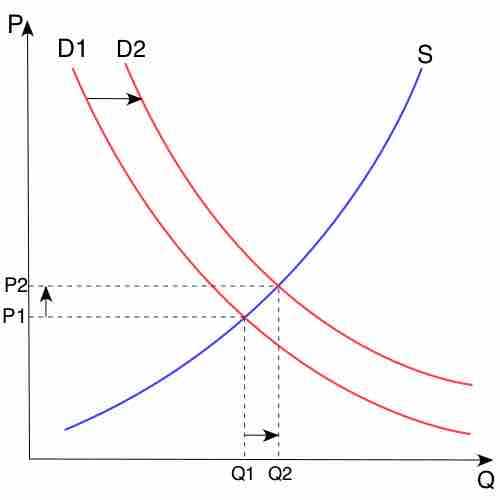
The demand curve shows how consumer choices respond to changes in price.
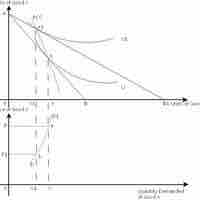
The law of demand pursues the derivation of a demand curve for a given product that benchmarks the relative prices and quantities desired.

The income effect and substitution effect combine to create a labor supply curve to represent the consumer trade-off of leisure and work.