Section 3
Long-Run Outcomes
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Economics
Economics
by Boundless
5 concepts
Long Run Supply Decisions
The long-run supply curve in a perfectly competitive market has three parts; a downward sloping curve, a flat portion, and an upwards sloping curve.
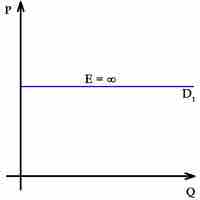
Long Run Market Equilibrium
The long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive market occurs when marginal revenue equals marginal costs, which is also equal to average total costs.
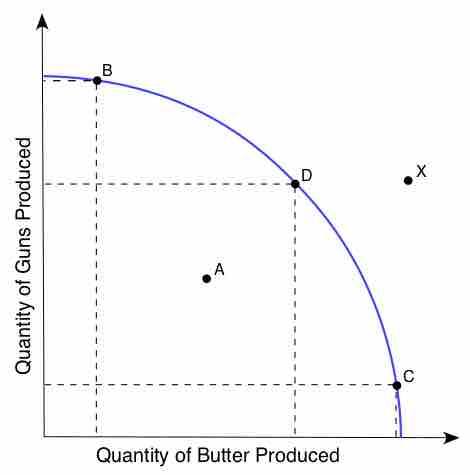
Productive Efficiency
Productive efficiency occurs when production of a good is achieved at the lowest resource cost possible, given the level of production of other goods.

Allocative Efficiency
Free markets iterate towards higher levels of allocative efficiency, aligning the marginal cost of production with the marginal benefit for consumers.
Entry and Exit of Firms
The absence of barriers of entry and exit is a necessary condition for a market to be perfectly competitive.