Chapter 5
Learning to Listen and Helping Others Do the Same
By Boundless

Listening is an active process by which we make sense of, assess, and respond to what we hear.

Critical thinking skills are essential and connected to the ability to listen effectively and process the information that one hears.

Listening is negatively affected by low concentration, trying too hard, jumping ahead, and/or focusing on style instead of substance.

The first stage of the listening process is the receiving stage, which involves hearing and attending.

The understanding stage is the stage during which the listener determines the context and meanings of the words that are heard.

The evaluating stage is the listening stage during which the listener critically assesses the information she's received from the speaker.

The responding stage is when the listener provides verbal and/or nonverbal reactions to what she hears.
The remembering stage occurs as the listener categorizes and retains the information she's gathering from the speaker.
Cultural differences between listeners and speakers can create barriers to effective communication.

All of us can and do speak the language of multiple gender cultures, and we can use this knowledge to communicate effectively.

Technology can assist the audience with listening, but can also be a distraction at the same time.

Resisting distractions and listening actively are two ways to become a more effective listener.

Open-minded listening requires empathy and a suspension of judgment on the part of the listener.
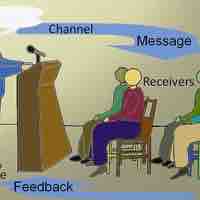
Feedback is the verbal and non-verbal responses from an audience which help the speaker modify and regulate what s/he is saying.

To hold the audience's attention, consider their readiness to perceive, the selection of stimuli, and how to maintain current awareness.
To maximize understanding, use general rhetorical strategies and other approaches that build upon the audience's prior experiences.

Aristotle established three methods of proof to build credibility: initial, derived, and terminal.

Encoding (or registration), storage, and recollection comprise the three main stages in the formation and retrieval of memory.

When giving criticism, it is important to keep in mind cultural differences such as eye contact, verbal style, and speaker expectations.

Effective criticism should be positively intended, specific, objective, and constructive in order to achieve results.
When receiving criticism try to be: accepting, open-minded, and willing to seek clarity.