Elements of Speech Communication: The Channel
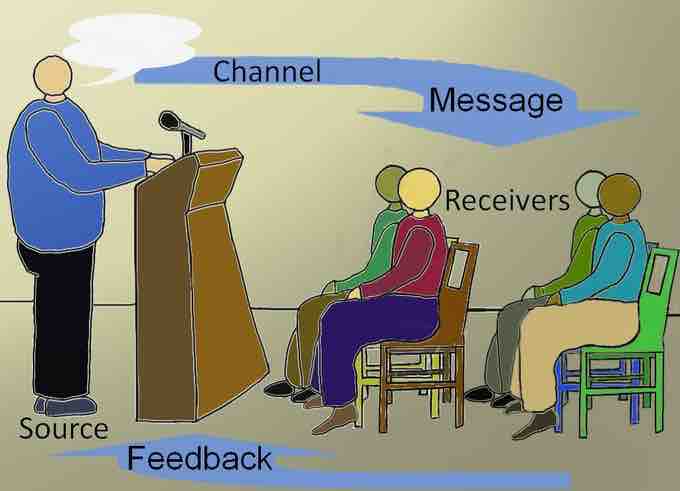
A simple speech communication model includes a sender (that is, a speaker), a message, a receiver (that is, an audience), and a channel. Claude Shannon, who developed one of the earlier communication models, defined the channel as the medium used to transmit the signal from the transmitter to the receiver. In a face-to-face, in-person speaking situation, the channel will be primarily audio using sound and visual using light waves; in a speaking situation with a remote audience via videoconferencing, the channel will be computer mediated audio and visual.
Communication Channel Model
The speaker uses a channel to transmit the message to the audience.
Face-to-Face, Co-Located Audience Channel
When speaking to an audience in person, a speaker uses both verbal and non-verbal methods to communicate the message. The sounds that a speaker makes are interpreted as words. The sounds are transmitted through an audio (or auditory) channel as sound waves and are received by the listeners in the audience. Speakers also use their hands to make gestures, change their facial expressions, and project images or words on a screen. These cues are received by the listeners through the visual part of the channel: their sense of sight. When the speaker and the audience are in the same room at the same time, the channels of communication are synchronous, in real time.
Computer Mediated Communication (CMC) Channel
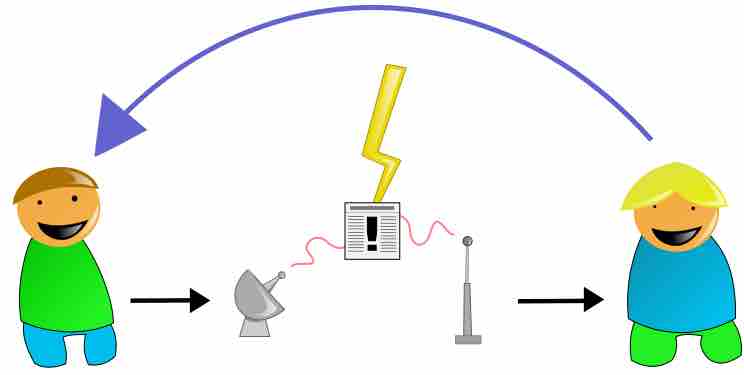
Speakers also use communication channels that are mediated, meaning there is something between the speaker and the receivers. In some cases, the auditory and visual signal is mediated by a computer to convert what the speaker says and does into a digital signal that is transmitted to remote audiences. Computer Mediated Communication (CMC) is able to overcome physical and social limitations of other forms of communication, and therefore allow the interaction of people who are not physically sharing the same space. Computer mediated digital channels may be synchronous, when remote audiences are listening to the speech via computer conferencing or streaming audio and video at the same time the speech is being delivered. The channel might also be asynchronous, when audiences listen to the speech at some time after the speech was delivered, perhaps via a website like youtube.com or vimeo.com. The message delivered through CMC channels could be only audio, but is likely to involve both audio and video, which uses the auditory and visual senses of the humans to decode the digital signals and process the message.
Shannon Weaver Communication Model
The channel in the middle links the speaker with the receiver of the message.