Traditional profit optimization includes methods for reduction of pricing, promotional, and markdown losses.
Yield management can help firms optimize profits. Firms that engage in yield management usually do so via computer yield management systems, and periodically review transactions for goods or services already supplied as well as those being supplied in the future. They may also review information (including statistics) about events (known future events such as holidays, or unexpected past events such as terrorist attacks), competitive information (including prices), seasonal patterns, and other pertinent factors affecting sales. The models use market segment and price point to forecast total demand for all products or services they provide. Since total demand normally exceeds what the particular firm can produce in that period, the models attempt to optimize the firm's outputs to maximize revenue. This optimization seeks to address key questions, such as: "Given our operating constraints, what is the best mix of products and/or services for us to produce and sell in the period; and at what prices do we sell those products and/or services to generate the highest expected revenue? " Optimization can help the firm adjust prices and allocate capacity among market segments to maximize expected revenues. This can be done at different levels:
- By goods (such as a seat on a flight or a seat at an opera production)
- By group of goods (such as the entire opera house or all seats on a flight)
- By market (such as sales from Seattle and Minneapolis for a flight via Seattle-Minneapolis-Boston)
- Overall (such as on all routes of an airline, or on all seats during an opera production season)
Revenue optimization is a method of determining 'optimal' profits or expenditures, and can be related to quadratics, as the vertex of a parabola can illustrate the point where the ‘maximum' revenue can be attained. Revenue optimization requires finding the x-intercepts and vertex, which can be done utilizing the quadratic formula (x-intercepts), and completing the square (vertex/ maximum). By finding these, one can then determine the highest or lowest cost and where the costs and quantities must lie in accordance to the vertex. This method is effective for maximizing profits for companies and families, as it can ensure the highest profit for sales and the lowest amounts for expenditures.
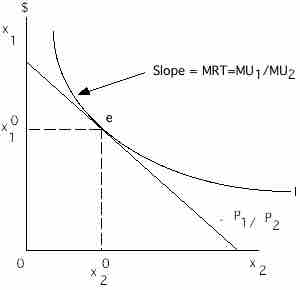
Optimization
Optimization point at x1, x2.