Chapter 21
Viruses
By Boundless
Viruses are infectious particles about 100 times smaller than bacteria and can only be observed by electron microscopy.
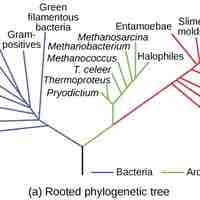
The evolution of viruses is speculative as they do not fossilize; biochemical and genetic information is used to create virus histories.
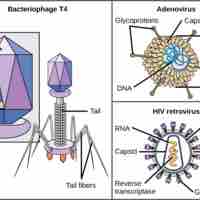
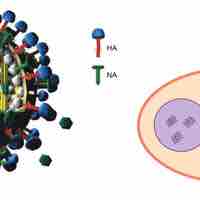
Viruses of all shapes and sizes consist of a nucleic acid core, an outer protein coating or capsid, and sometimes an outer envelope.
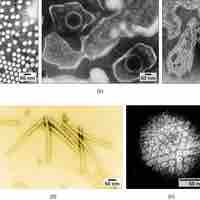
Viruses are classified by factors such as their core content, capsid structure, presence of outer envelope, and how mRNA is produced.
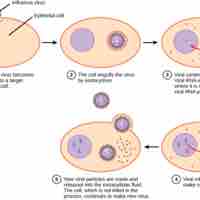
Viral infection involves the incorporation of viral DNA into a host cell, replication of that material, and the release of the new viruses.
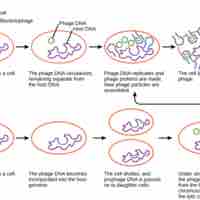
Bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, may undergo a lytic or lysogenic cycle.
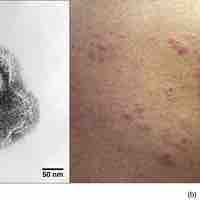
Animal viruses have their genetic material copied by a host cell after which they are released into the environment to cause disease.

Plant viruses can cause damage to stems, leaves, and fruits and can have a major impact on the economy because of food supply disruptions.