Chapter 29
Vertebrates
By Boundless
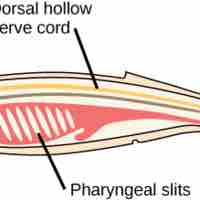
Animals in the phylum Chordata share four key features: a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail.
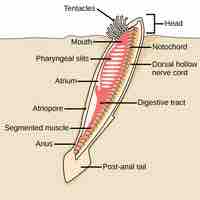
Chordata contains two subphylums of invertebrates: Urochordata (tunicates) and Cephalochordata (lancelets).
Both genomic and fossil evidence suggests that vertebrates evolved from craniates, which evolved from invertebrate chordates.

Vertebrata is a subphlyum of Chordata that is further defined by their bony backbone.

Amphibians evolved from fish 400 million years ago and are characterized by four limbs, moist skin, and sensitive inner ear structures.

Amphibians can be divided into three groups: Urodela (salamanders), Anura (frogs), and Apoda (caecilians).

The distinguishing characteristic of amniotes, a shelled egg with an amniotic membrane, allowed them to venture onto land.
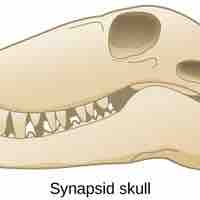
Modern amniotes, which includes mammals, reptiles, and birds, evolved from an amphibian ancestor approximately 340 million years ago.
Reptiles are ectothermic tetrapods that lay shelled eggs on land and possess scaly skin and lungs.
Dinosaurs and pterosaurs diverged from early amniotes and dominated the Mesozoic Era.

Class Reptilia, amniotes that are neither mammals nor birds, has four living clades: Crocodilia, Sphenodontia, Squamata, and Testudine.
Mammalian traits include, among others: specialized glands, modified jaw and inner ear bones, urinary bladder, and hair.

The modern mammals of today are synapsids: descendants of a group called cynodonts which appeared in the Late Permian period.

Living mammals can be classified in three subclasses: eutherian, metatherians and monotremes.
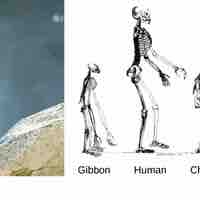
All primates exhibit adaptations for climbing trees and have evolved into two main groups: Prosimians and Anthropoids.
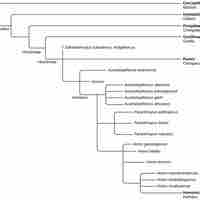
Modern humans and chimpanzees evolved from a common hominoid ancestor that diverged approximately 6 million years ago.
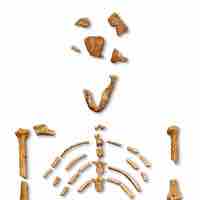
The hominin Australopithecus evolved 4 million years ago and is believed to be in the ancestral line of the genus Homo.

The human genus Homo, which includes modern humans as well as extinct human relatives, appeared around 2.3 million years ago.