Chapter 5
Structure and Function of Plasma Membranes
By Boundless
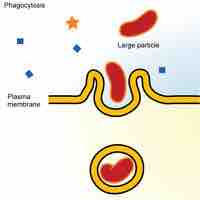
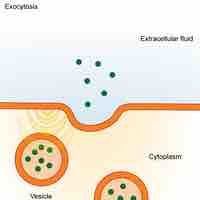
The plasma membrane protects the cell from its external environment, mediates cellular transport, and transmits cellular signals.
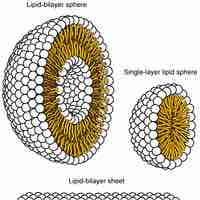
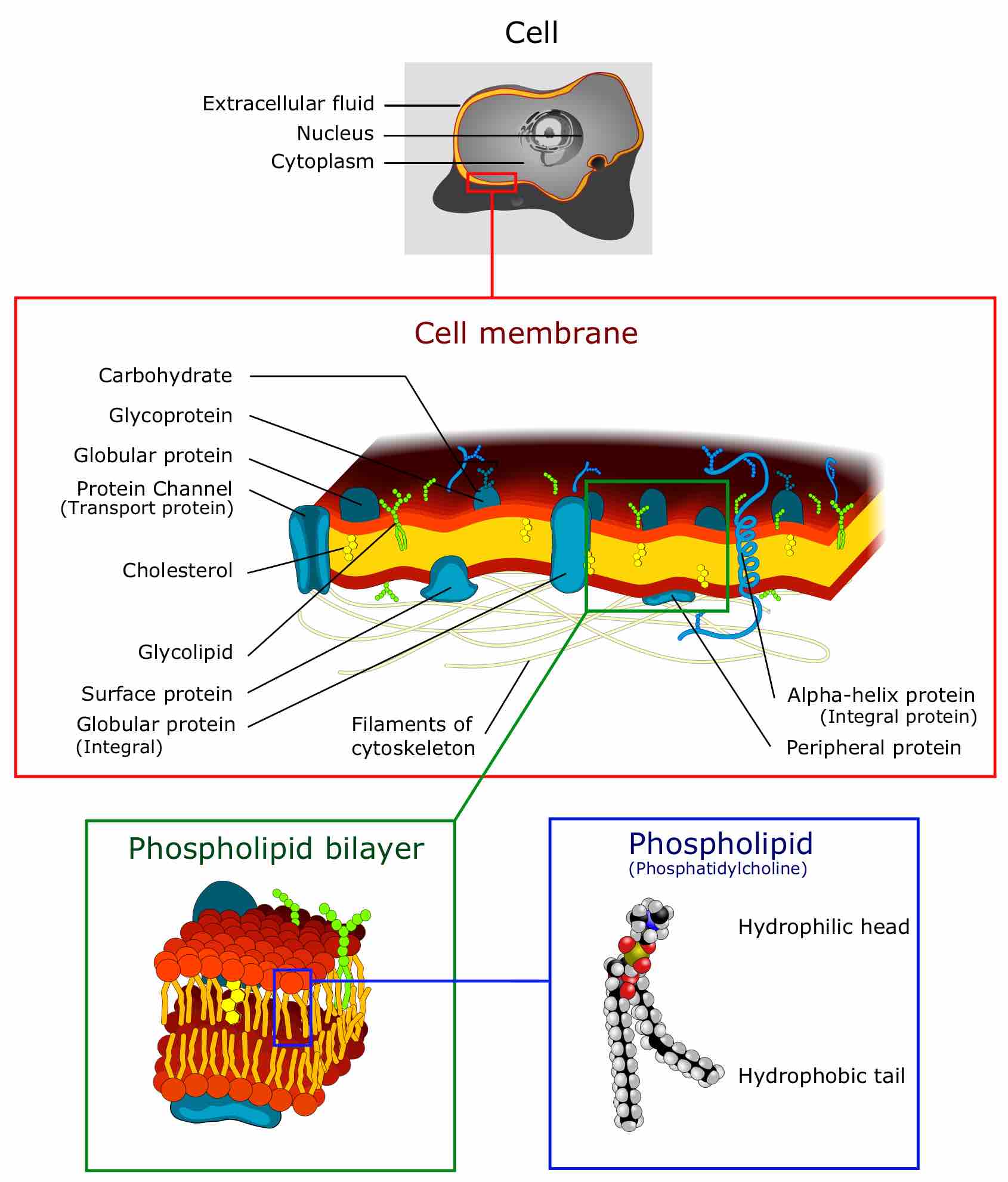
The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates.
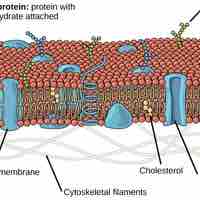
The mosaic nature of the membrane, its phospholipid chemistry, and the presence of cholesterol contribute to membrane fluidity.
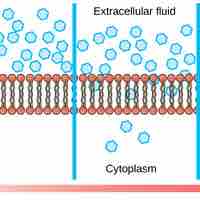
Passive transport, such as diffusion and osmosis, moves materials of small molecular weight across membranes.
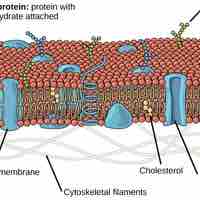
The hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions of plasma membranes aid the diffusion of some molecules and hinder the diffusion of others.
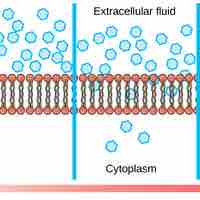
Diffusion is a process of passive transport in which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
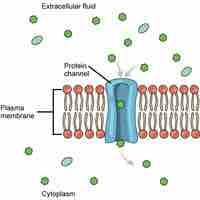
Facilitated diffusion is a process by which molecules are transported across the plasma membrane with the help of membrane proteins.
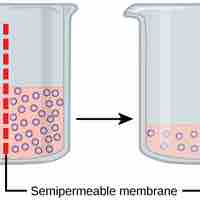
Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
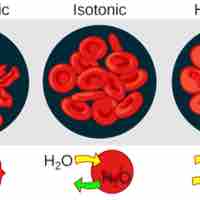
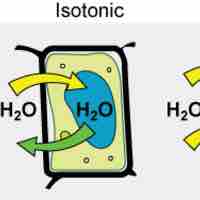
Tonicity, which is directly related to the osmolarity of a solution, affects osmosis by determining the direction of water flow.
Osmoregulation is the process by which living things regulate the effects of osmosis in order to protect cellular integrity.
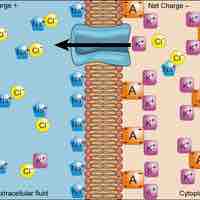
To move substances against the membrane's electrochemical gradient, the cell utilizes active transport, which requires energy from ATP.
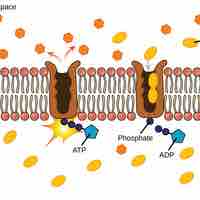
The sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of the cell.
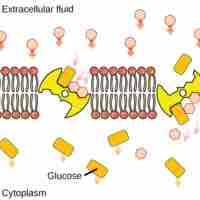
In secondary active transport, a molecule is moved down its electrochemical gradient as another is moved up its concentration gradient.
- Studying Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic Cells
- The Endomembrane System and Proteins
- The Cytoskeleton