Concept
Version 10
Created by Boundless
Age Structure, Population Growth, and Economic Development
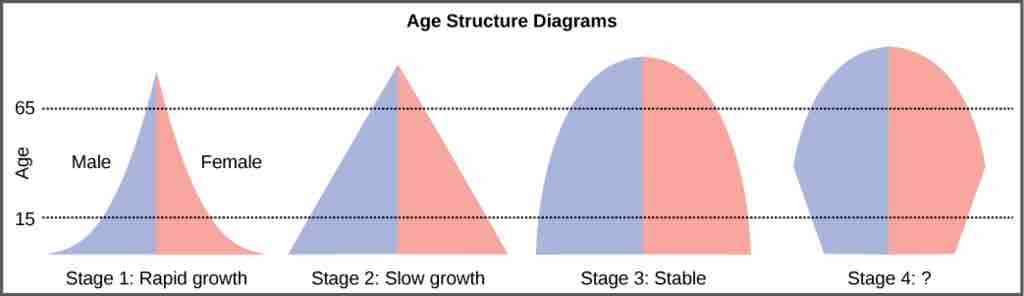
Population bar graphs for stages of demographic change from expansion to contraction
The leftmost diagram (representing the age structure of a rapidly-growing population) indicates that the number of individuals decreases rapidly with age. The slow-growth model shows that the proportion of individuals decreases steadily with age. The stable population diagram is rounded on top; the older part of the population is a larger proportion of the population than in the other age diagrams. The rightmost diagram represents a population that may be stable or even declining. The relatively few young people may not be making up for the mortality among the older age groups.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"OpenStax College, Human Population Growth. October 17, 2013."
http://cnx.org/content/m44875/latest/Figure_45_05_03.png
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.