Chapter 41
Osmotic Regulation and the Excretory System
By Boundless
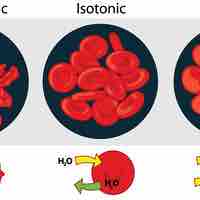
Osmoregulation balances concentrations of solutes and water across semi-permeable membranes, maintaining homeostasis.
Ions cannot diffuse passively through membranes; instead, their concentrations are regulated by facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Solution concentration is expressed by a solution's molality, while electrolyte concentration is expressed in terms of milliequivalents per liter.
Aquatic organisms with various salt tolerances adapt to their environments through osmoregulation and osmoconformation.
Urea, a nitrogenous waste material, is the end product excreted in urine when ammonia is metabolized by animals, such as mammals.
Birds and reptiles have evolved the ability to convert toxic ammonia into uric acid or guanine rather than urea.
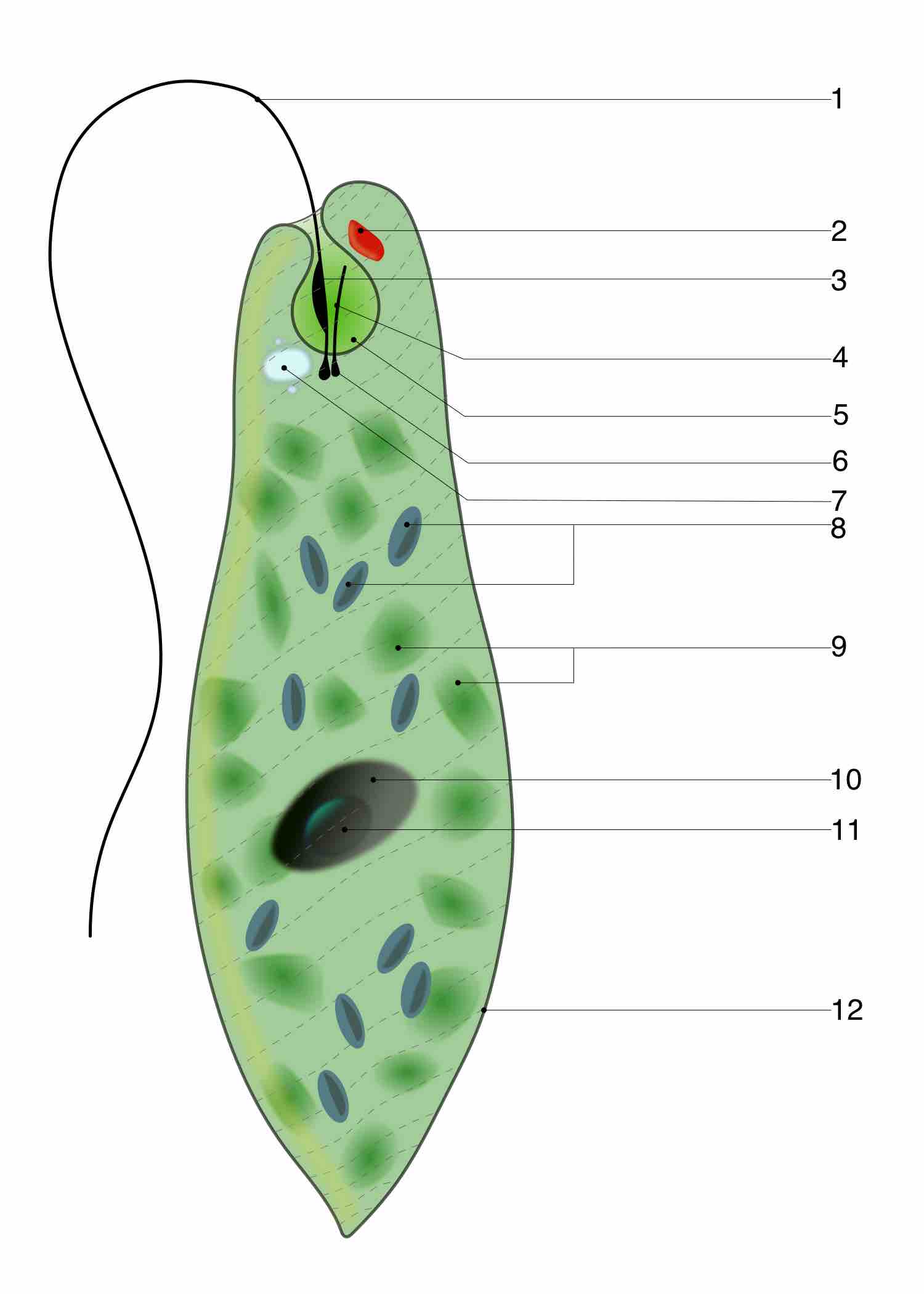
Contractile vacuoles absorb excess water and wastes from a microorganism's cell and excrete them into the environment by contracting.
Flame cells and nephridia remove the waste from bodies through filtration in a manner similar to a kidney.
Malpighian tubules remove wastes from insects by producing urine and solid nitrogenous waste, which are then excreted from the body.
The kidneys regulate the body's osmotic pressure in mammals.

The functional unit of the kidney, the nephron, removes waste from the body.
Urine is a byproduct of the osmoregulatory function of kidneys, which filter blood, reabsorb water and nutrients, and secrete wastes.
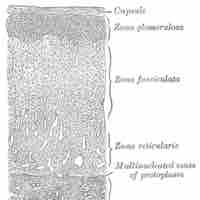
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are released during the flight/fight response, causing vasoconstriction of blood vessels in the kidney.
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) stabilizes blood pressure and volume via the kidneys, liver, and adrenal cortex.