Chapter 12
Mendel's Experiments and Heredity
By Boundless

While working with pea plants, Gregor Mendel noticed that offspring were similar to their parent plants, which led him to some of the earliest theories about genetics.

The garden pea has several advantageous characteristics that allowed Mendel to develop the laws of modern genetics.
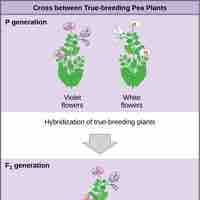
Mendel's crosses involved mating two true-breeding organisms that had different traits to produce new generations of pea plants.
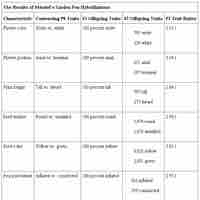
Mendel's experiments with peas revealed the presence of dominant and recessive traits in the filial generations.
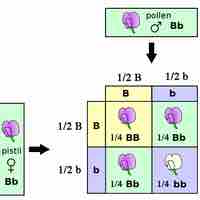
The rules of probability can be applied to Mendelian crosses to determine the expected phenotypes and genotypes of offspring.

Genes exist in pairs within an organism, with one of each pair inherited from each parent.

The observable traits expressed by an organism are referred to as its phenotype and its underlying genetic makeup is called its genotype.
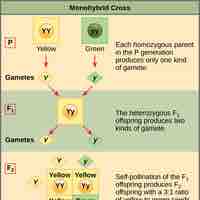
A Punnett square applies the rules of probability to predict the possible outcomes of a monohybrid cross and their expected frequencies.
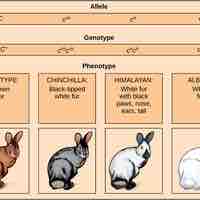
With the inclusion of incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, and mutant alleles, the inheritance of traits is complex process.
A gene present on one of the sex chromosomes (X or Y in mammals) is a sex-linked trait because its expression depends on the sex of the individual.
Inheriting two copies of mutated genes that are nonfunctional can have lethal consequences.
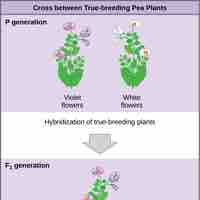
Mendel formed the Laws of Heredity (the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment) from his pea plant experiments.

In a heterozygote, the allele which masks the other is referred to as dominant, while the allele that is masked is referred to as recessive.

Mendel's Law of Segregation states that a diploid organism passes a randomly selected allele for a trait to its offspring, such that the offspring receives one allele from each parent.
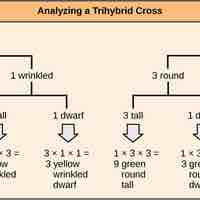
Independent assortment allows the calculation of genotypic and phenotypic ratios based on the probability of individual gene combinations.
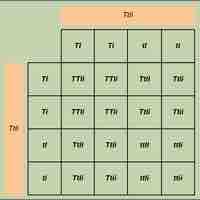
Genes that are on the same chromosome, or "linked", do not assort independently, but can be separated by recombination.
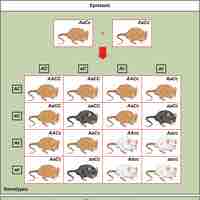
Epistasis occurs when one gene masks or interferes with the expression of another.