Chapter 47
Conservation Biology and Biodiversity
By Boundless
Human activity is the driving force behind the current biodiversity crisis, which is causing great species loss in a short time period.
Genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and human-derived diversity are measures of biodiversity that currently define life on earth.
Biodiversity has been affected by five mass extinction periods, which greatly influenced speciation and extinction rates.
Biodiversity loss, especially the disappearance of megafauna, during the Pleistocene Extinction has been linked to the arrival of humans.
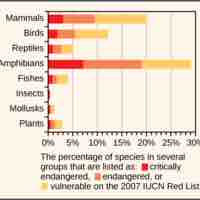
Human activities probably caused the Holocene mass extinctions; many methods have been employed to estimate these extinction rates.
Maintaining biodiversity ultimately helps maintain of human health; many medicines are derived from plants and, recently, animal toxins.
Maintaining genetic biodiversity of wild species of our crops that are related to domesticated species ensures our continued food supply.
Overfishing leads to fishery extinctions, loss of a food source, and affects many other species in ways that may be impossible to predict.
Through increased adoption of sustainable practices, we can reduce habitat loss and its consequences.
Overharvesting threatens biodiversity by degrading ecosystems and eliminating species of plants, animals, and other organisms.
Exotic species introduced into foreign ecosystems can threaten native species through competition for resources, predation, and disease.
The global warming trend is recognized as a major biodiversity threat, especially when combined with other threats such as habitat loss.
Technology has matured to the point where we can begin cataloging the planet's species in accessible ways; DNA barcoding is one such method.
Human responses to climate change and species loss include national and international legal measures, as well as the creation of preserves.
The purpose of ecological restoration projects, such as wildlife and ecosystem preserves, is to return ecosystems to pre-disturbance states.