Overview: Versailles
The Palace of Versailles is an opulent palace built by Louis XIV that contains 700 rooms, extensive gardens, and lavish decoration. Initially a small hunting lodge built by his father, Louis XIV transformed Versailles with four intensive building campaigns over his reign. The formal aesthetic of the palace was meant to glorify France and show the power and greatness of the self-proclaimed Sun King, Louis XIV. The architect for the palace was Louis Le Vau, the interior decorator was Charles Le Brun, and the landscape designer was Andre Le Notre. These three artists had worked together previously on the private Chateau Vaux le Vicomte for the king's minister of finance before he was imprisoned. In 1682, Versailles was transformed into the official residence of the king, and such notable features of the palace as the Hall of Mirrors and the Grande Canal were built.
The Art and Artists of Versailles
The Architecture: Louis Le Vau
The Palace of Versailles was executed in the French Baroque style by architect Louis Le Vau, a French Classical architect who worked for King Louis XIV. French Baroque architectural style is characterized by its large curved forms, twisted columns, high domes, and complicated shapes. In comparison to the Baroque architecture of the rest of Europe, it is commonly thought to be more restrained and characterized by its mixture of lavish details on symmetrical and orderly buildings.
The Interior Design: Charles Le Brun
Charles Le Brun was the interior decorator for the Palace of Versailles, as well as first painter to the king. Louis XIV declared Le Brun the "greatest painter of all time," and Le Brun worked on such notable features of the palace as the Halls of War and Peace, the Ambassadors' Staircase, and the Great Hall of Mirrors. Interior design from this period is known as Louis XIV style, originated by Le Brun, and was characterized by richly woven red and gold fabrics or brocades, heavy gilded plaster molding, large sculpted side boards, and heavy marbling.
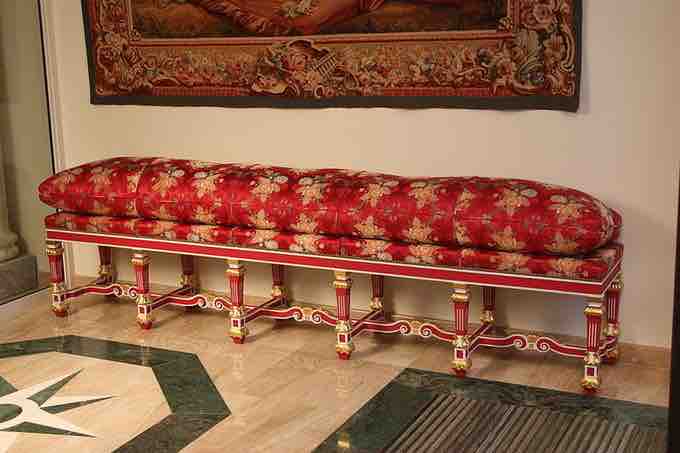

Louis XIV style
The style of Louis XIV at Versailles is characterized by richly woven red and gold fabrics or brocades, heavy gilded plaster molding, large sculpted side boards, and heavy marbling.
The Hall of Mirrors is the central gallery of the Palace of Versailles and is one of the most famous rooms in the world. The main feature of this room is a series of 17 mirrored arches that reflect 17 arcaded windows overlooking the gardens. Each arch contains 21 mirrors. The arches are fixed between marble pilasters upon which bronze symbols of France are embedded.
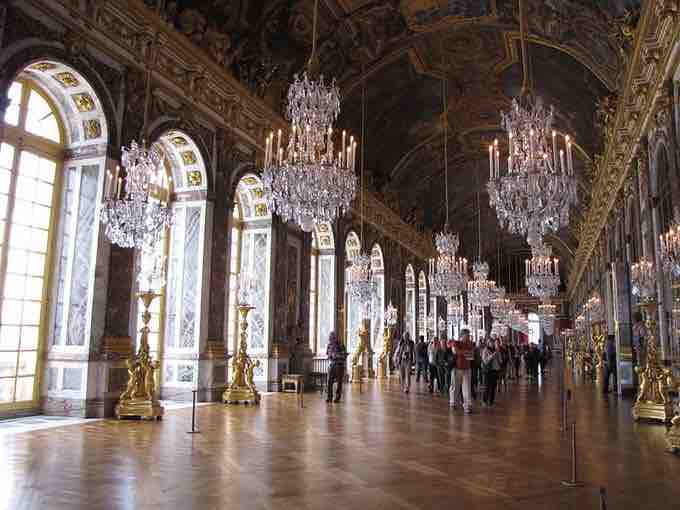

The Hall of Mirrors
The main feature of the Hall of Mirrors is a series of 17 mirrored arches that reflect 17 arcaded windows overlooking the gardens. Each arch contains 21 mirrors.
The Gardens: Andre Le Notre
The landscape design at the Palace of Versailles is one of the most extravagant in history. Headed by Andre Le Notre, the gardens at Versailles cover nearly 2,000 acres of land and were executed in the French formal garden style, or jardin a la francaise. This style is characterized by its meticulously manicured lawns, parterres of flowers, numerous fountains, and sculptures.
A common feature of sculpture and decoration at Versailles is the use of classical mythology as allegory. The Bassin de Latone was designed by Le Notre and sculpted by Gaspard and Balthazar Marsy between 1668–1670. This fountain depicts scenes from Ovid's Metamorphoses, chosen as allegories to revolts during the king's reign. The Bassin d'Apollon is another fountain that depicts the sun god driving his chariot to light the sky. The Grotte de Thetys is a freestanding structure with an interior decorated in elaborate shell-work to represent the myth of Apollo.
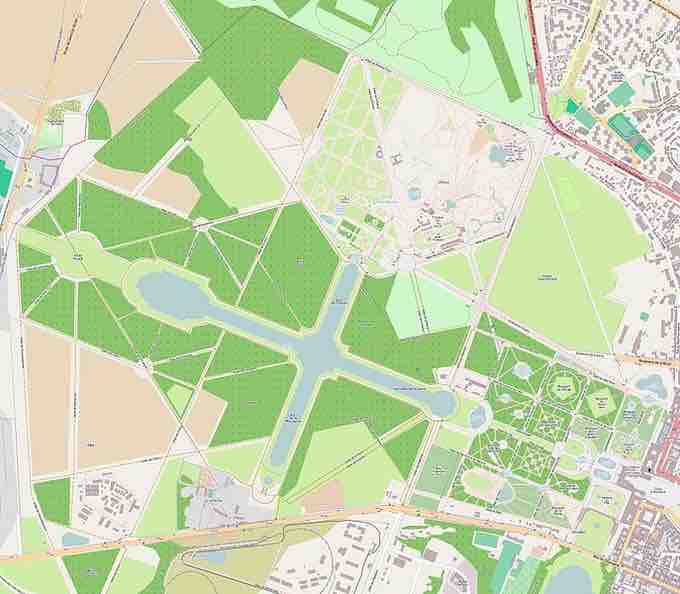
Gardens at Versailles
Plan for the extravagant gardens at the Palace of Versailles.
The Grande Canal is a notable feature of the gardens, with an impressive length of 1,500 x 62 meters. King Louis XIV ordered the construction of "little Venice" on the Grand Canal, which housed yachts, gondolas, and gondoliers received from Venice. It also served a functional purpose by gathering the water that drained from the fountains and redistributing it to the gardens by horse-powered pump.
The Grande Commande is a series of 24 statues that were commissioned by Louis XIV to decorate the gardens. The statues illustrate the classic quaternities (sets of 4) at the time of the Four Humors, the Four Parts of the Day, the Four Parts of the World, The Four Forms of Poetry, the Four Elements, and the Four Seasons. Four additional sculptures depict abductions from classical mythology.