Earnings Per Share
Earnings per share (EPS) is the amount of earnings per each outstanding share of a company's stock. In the United States, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) requires that companies' income statements report EPS for each of the major categories of the income statement: continuing operations, discontinued operations, extraordinary items, and net income.
The EPS formula does not include preferred dividends for categories outside of continued operations and net income. Earnings per share for continuing operations and net income are more complicated; any preferred dividends are removed from net income before calculating EPS. This is because preferred stock rights have precedence over common stock. If preferred dividends total $100,000, then that money is not available to distribute to each share of common stock.
Earnings Per Share (Basic Formula): ""
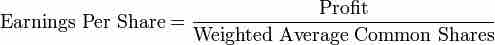
Earnings Per Share
Basic formula
Earnings Per Share (Net Income Formula): ""

Earnings Per Share
Net income formula
Earnings Per Share (Continuing Operations Formula): ""
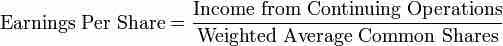
Earnings Per Share
Continuing operations formula
Only preferred dividends actually declared in the current year are subtracted. The exception is when preferred shares are cumulative, in which case annual dividends are deducted regardless of whether they have been declared or not. Dividends in arrears are not relevant when calculating EPS.
Diluted Earnings Per Share (diluted EPS) is a company's earnings per share (EPS) calculated using fully diluted outstanding shares (i.e. including the impact of stock option grants and convertible bonds). Diluted EPS indicates a "worst case" scenario, one in which everyone who could have received stock without purchasing it directly for the full market value did so.
To find diluted EPS, basic EPS is first calculated for each of the categories on the income statement. Then each of the dilutive securities are ranked based on their effects, from most dilutive to least dilutive and antidilutive. Then the basic EPS number is diluted one by one by applying each, skipping any instruments that have an antidilutive effect.
Calculations of diluted EPS vary. Morningstar reports diluted EPS "Earnings/Share $" (net income minus preferred stock dividends divided by the weighted average of common stock shares outstanding over the past year). This is adjusted for dilutive shares. Some data sources may simplify this calculation by using the number of shares outstanding at the end of a reporting period.